Microsoft ends support for Internet Explorer on June 16, 2022.
We recommend using one of the browsers listed below.
- Microsoft Edge(Latest version)
- Mozilla Firefox(Latest version)
- Google Chrome(Latest version)
- Apple Safari(Latest version)
Please contact your browser provider for download and installation instructions.
February 20, 2025
NTT Corporation
World's first: NTT, Nokia, and Anritsu successfully demonstrate dynamic rerouting of mobile fronthaul using IOWN All-Photonics Network (APN)
Aiming to realize a power efficient RAN network by dynamic base station operation according to traffic fluctuations
News Highlights:
- Based on the IOWN Global Forum architecture, the IOWN APN was successfully applied to the mobile fronthaul between the antenna unit (Radio Unit, RU) and the control unit (Distributed Unit, DU) of a 5G RAN base station, demonstrating dynamic rerouting.
- This technology enables highly power efficient and robust networks.
TOKYO - February 20, 2025 - NTT Corporation (Headquarters: Chiyoda Ward, Tokyo; Representative Member of the Board and President: Akira Shimada; hereinafter "NTT"), in collaboration with Nokia Corporation and Anritsu Corporation, has demonstrated that dynamic rerouting of the mobile fronthaul is possible by using the IOWN All-Photonics Network (APN)1. In the demonstration, we applied APN to the mobile fronthaul between the antenna unit (Radio Unit, RU) and the control unit (Distributed Unit, DU) of a 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) base station. The results confirmed that in an environment where user traffic flows through two mobile fronthaul using the IOWN APN, the dynamic route change takes less than eight minutes and does not affect user traffic beyond the changed route. Traffic flows normally, even after the change. This achievement allows flexible DU switching in response to mobile traffic fluctuation, enabling DU base consolidation and activation of only necessary DU base, reducing power consumption, Additionally, in the event of a route failure, routes can be swiftly switched to alternative DU base, thereby reducing the impact on services and contributing to improved network reliability.
Background of the study
With the rise of 5G technology, mobile traffic is increasing, leading to higher power consumption of base stations and communication facilities. The advent of 6G is expected to deliver even faster communications and large amounts of data transmission, further amplifying power consumption. As a result, improving power efficiency is an important issue for mobile carriers and mobile vendors. To address this challenge, various solutions have been implemented, including reducing base station power consumption, applying virtualization technology.
This initiative aims to further reduce the power consumption of base stations and communications facilities while improving the reliability of the network through dynamic routing. Mobile traffic fluctuates depending on human movement and time of day—business districts experience peak demand during daytime hours, whereas nighttime traffic is lower requiring fewer DUs. However, under the current fixed, point-to-point optical fiber connection (dark fiber) between RU and DU, operators run more DUs than necessary, and the connected DUs must always remain operational to maintain service.
By leveraging the IOWN APN for the mobile front haul, RUs can dynamically reroute connections to DUs, from a point-to-point physical connection between RU and the DU. This enables all DU bases to function when the mobile traffic is high and allows the system to switch to fewer DUs when demand decreases, consolidating resources while maintaining service. Additionally, DU bases that are no longer needed due to the consolidation can be shut down to reduce power consumption—not just for communication equipment but also for the entire base including air conditioning. Moreover, in the vent of failure between an RU and a DU, dynamic rerouting allows the system to bypass the affected link and swiftly switch to an operational DU base. This ensures continuous service coverage by the RU, enhancing network reliability.
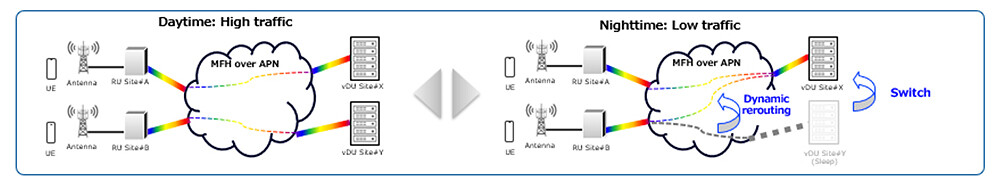 Figure 1 Dynamic Routing Using APN for Mobile Fronthaul
Figure 1 Dynamic Routing Using APN for Mobile Fronthaul
Outline of the demonstration experiment
In this demonstration, we examined a procedure that optimally combines RU changes and APN route changes in order to minimize communication impact during dynamic route adjustments. We verified that dynamic route changes could be performed successfully using this procedure.
For verification, IOWN APN was applied at 30 km between two mobile fronthaul points. The test environment simulated real-time user traffic while modifying the RU settings of the DU device and adjusting the optical path switching of the APN device. We assessed the time required for dynamic route changes, their impact on communication, and post-switching communication quality.
The verification was conducted following the IOWN APN device configuration and transmission method from the IOWN Global Forum's2 Proof of Concept (PoC) Reference3, IOWN for mobile networks.
Results of the demonstration experiment
Verification tests confirmed that dynamic route changes can be completed in less than eight minutes4 over a transmission distance of 30 km. Communication quality remained unaffected, including data transfer speed and loss rate after switching. Although user traffic on the changed route was interrupted, but other routes remained unaffected. Power consumption was reduced by approximately 20%5 before and after changing the route.
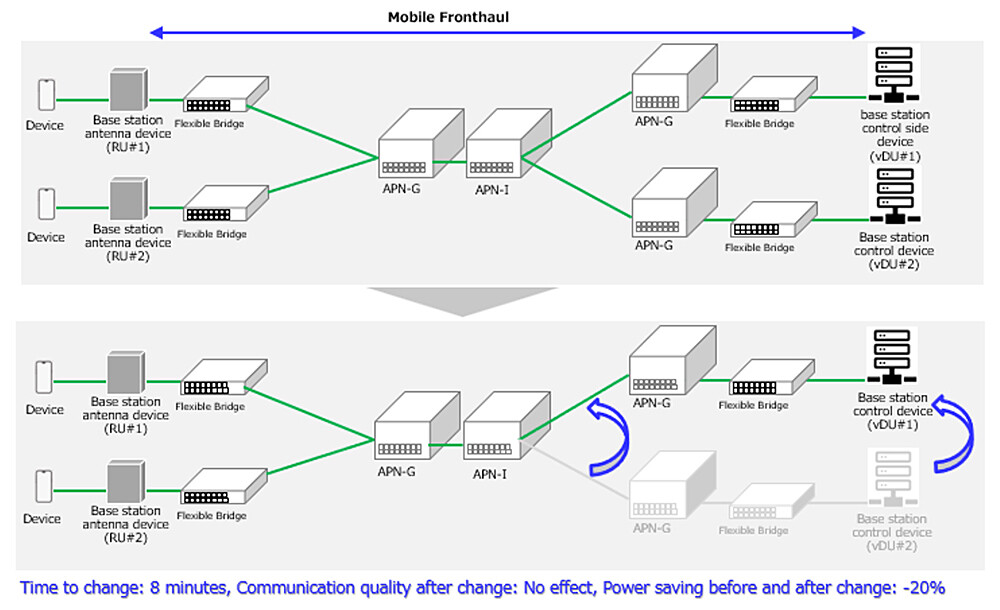 Figure 2 Demonstration Environment and Results
Figure 2 Demonstration Environment and Results
Role of each company in the demonstration experiment
We conducted a dynamic routing demonstration using IOWN APN (Figure 2) as outlined below.
Outlook
This demonstration confirmed that dynamic rerouting can be successfully performed using IOWN APN for mobile fronthaul. This enables dynamic DU base operations during mobile traffic fluctuations and failures, reducing power consumption and service impact. Moving forward, we plan to conduct a demonstration experiment on the power reduction effect of IOWN's dynamic route changes and shorten the time required for dynamic rerouting to minimize the impact on service. These experiments will simulate real-world base station configuration, number of users, traffic, and automatic route change decisions based on traffic prediction, aiming to achieve a highly power-efficient and resilient network.
1.IOWN APN (All Photonics Network): The IOWN consists of three main components: the All-Photonics Network (APN), which introduces optical-based technologies into everything from networks to devices; the Digital Twin Computing, which enables advanced real-time interaction between objects and people in cyberspace; and the Cognitive Foundation, which efficiently deploys various ICT resources including these.
By integrating new optical technologies into the networks, devices, and chips, APN achieves ultra-low power consumption and ultra-high-speed processing, which were previously difficult to achieve. By allocating wavelengths for each function on a single optical fiber, APN enables multiple functions that support social infrastructure, such as information communication, internet and sensing functions, without interference.
https://www.rd.ntt/e/iown/
2.IOWN Global Forum (IOWN GF): A forum that promotes the realization of a new communication infrastructure consisting of All-Photonics Networks including silicon photonics, edge computing, and wireless distributed computing. The forum focuses on developing new technologies, frameworks, technical specifications, and reference designs to meet future data and information processing requirements.
https://iowngf.org/
https://group.ntt/en/newsrelease/2019/10/31/191031a.html
3.PoC Reference of IOWN for mobile network: The technical studies in the mobile network area within the IOWN Global Forum.
https://iowngf.org/wp-content/uploads/formidable/21/IOWN-GF-RD-MFH_over_APN_PoC_Reference_1.0.pdf
4.Time that can be achieved by reducing working time and verification time through automation.
5.Approximate value. Demonstrated load with minimal user traffic and no variation.
About NTT
NTT contributes to a sustainable society through the power of innovation. We are a leading global technology company providing services to consumers and businesses as a mobile operator, infrastructure, networks, applications, and consulting provider. Our offerings include digital business consulting, managed application services, workplace and cloud solutions, data center and edge computing, all supported by our deep global industry expertise. We are over $93B in revenue and 330,000 employees, with $3.6B in annual R&D investments. Our operations span across 80+ countries and regions, allowing us to serve clients in over 190 of them. We serve over 75% of Fortune Global 100 companies, thousands of other enterprise and government clients and millions of consumers.
Media contact
NTT Corporation
Research and Development Market Strategy Division
Research and Development Planning Department
Inquiry form
Information is current as of the date of issue of the individual press release.
Please be advised that information may be outdated after that point.
NTT STORY
WEB media that thinks about the future with NTT