Microsoft ends support for Internet Explorer on June 16, 2022.
We recommend using one of the browsers listed below.
- Microsoft Edge(Latest version)
- Mozilla Firefox(Latest version)
- Google Chrome(Latest version)
- Apple Safari(Latest version)
Please contact your browser provider for download and installation instructions.
April 12, 2016
Improving Reliability of the System of Traffic Congestion Predictions and Traffic Signal Control Simulations through Nonstop Big Data Analysis --Quick, low-cost, reliable services provided by MAGONIA--
Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation (headquartered in Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, CEO Hiroo Unoura, NTT hereinafter) has proved that the distributed processing technology of the "MAGONIA*1", a new server architecture, improves reliability (fault-tolerance) and scalability of the system of traffic congestion predictions and traffic signal control simulations which is developed by NTT DATA Corporation (headquartered in Koto-ku, Tokyo, CEO Toshio Iwamoto, NTT DATA hereinafter.)
Joint experiments have established how MAGONIA can be applied to kinds of spatial analysis systems such as traffic congestion predictions and traffic signal control simulations. They have also confirmed that MAGONIA is effective in a wide range of applications.
We will apply the MAGONIA to wide variety of applications and use the MAGONIA to support service providers who need service reliability and scalability.
Background
NTT works on our new server architecture MAGONIA as part of the NetroSphere, a concept*2 of a future network R&D. A key MAGONIA component is its middleware, a distributed processing base (DPB). The DPB makes it possible to process large amounts of data at high speed, not to stop at any time, and to make processing power and functionality more flexible. In this way it meets the common needs for a variety of services, not limited to telecom services. Developing service on the DPB enables the service provider to concentrate just on the development of service logic, thus making it possible to deliver more reliable services faster at lower cost.
We have promoted the MAGONIA in the telecom field through the approval of the ETSI*3 NFV ISG*4 proof-of-concept framework*5, field trial for video delivery service use cases, and so on with our business partners. Furthermore, we have extended the scope of the MAGONIA to applications in fields other than telecommunications.
Overview of joint experiments
As shown in Fig. 1, the system of traffic congestion predictions and traffic signal simulations*6 developed by NTT DATA makes use of large amounts of sensor data collected in real time. It analyzes traffic trends (traffic simulation hereinafter) and controls traffic signals on the basis of the traffic simulation results. The system is required to have high scalability since the traffic simulation involves a large amount of calculation, which may change from time to time in accordance with changes in traffic volume. It is also required to have high reliability (fault tolerance) and real-time operability since it is essential to provide feedback to the traffic signals within the determined time limit.
The joint experiments with NTT DATA commenced in September 2015 to step toward a practical use of the system of traffic congestion predictions and traffic signal simulations. In them we evaluated how the MAGONIA's DPB could be applied to the existing system, and the reliability and the like of the system.
For the experiments the traffic simulation unit was successfully ported on the MAGONIA's DPB. This confirmed that scalability, reliability, and real-time operability were improved while using existing application logic. In this way it was shown that the MAGONIA is effective for a wide range of applications. Moreover, MAGONIA's DPB achieves a cost saving by playing a role in design, implementation, operation, and maintenance of the system in terms of scalability, reliability, and real-time operability without effects on application logic, leading to a reduction of development scale and operation.
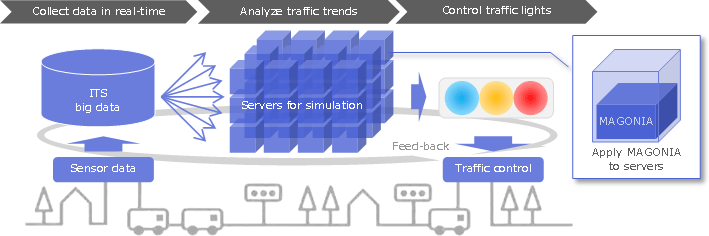 Fig.1. Applying the MAGONIA's DPB to the traffic simulation
Fig.1. Applying the MAGONIA's DPB to the traffic simulation
Future prospects
NTT will use the MAGONIA to support providers of services which requires processing large amounts of data at high speed, not stopping at any time, and making processing power and functionality more flexible including NTT DATA's traffic congestion predictions and signal control simulations. In this way we will contribute to improvements of service reliability and business solutions of service providers.
Reference: joint experiment details
The traffic simulation in the traffic congestion predictions and traffic signal simulations system (Fig. 1) differs in terms of operation characteristics from the telecom services that have to date demonstrated the effectiveness of the MAGONIA's DPB. As shown in Fig. 2, telecom services start processing at the moment that events such as transmission from the terminal are triggered; the load is balanced as a unit of the processing. Since the unit processing is by nature independent, distributed processing and data have a sparse relationship vis-à-vis each other. However, since the traffic simulation splits one processing (space) into multiple small processing (cells), the distributed processing and data are not fully independent. Accordingly, it is necessary to synchronize them. Furthermore, the processing is performed cyclically rather than at the moment the event is triggered.
This was the first time to mount a processing capability of this type on the MAGONIA's DPB. As shown in Fig. 3, by preparing the cell splitting function and the server-to-server processing synchronization function as an adapter between the application and the MAGONIA's DPB, the existing analysis logic can be installed in the DPB. The impact on the synchronization process performance has been a matter of concern, but experiment results confirmed that the traffic simulation could be completed within the determined time limit. Moreover, even if a server fails when performing the traffic simulation, it was confirmed that the failover procedure can continue to analyze quickly for multiple servers on a cell-by-cell basis. It was also confirmed that the system's computational capabilities could be dynamically scaled during the simulation process. In addition, since this architecture is not application dependent, it is expected to be similarly effective for a variety of applications with similar characteristics.
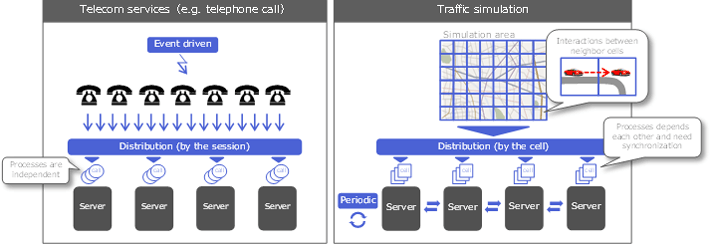 Fig.2. A difference between telecom services and the traffic simulation
Fig.2. A difference between telecom services and the traffic simulation
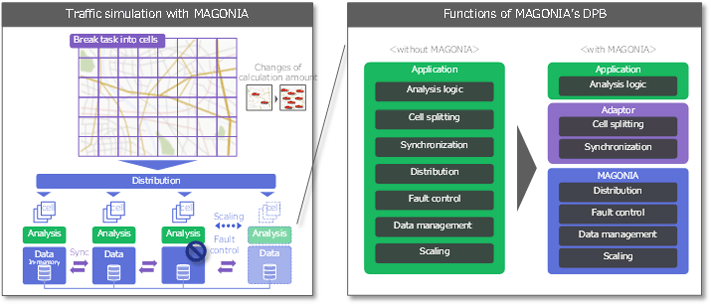 Fig.3. Details of the traffic simulation with the MAGONIA's DPB
Fig.3. Details of the traffic simulation with the MAGONIA's DPB
Glossary
*1MAGONIA MAGONIA is a registered trademark of NTT.
*2NetroSphere
Proposed as a concept for the future technical development of communication networks
Reference: http://www.ntt.co.jp/news2015/1502e/150219a.html
*3ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) A standards body established to produce telecommunications specifications in the European bloc
*4NFV ISG (Network Functions Virtualisation Industry Specification Group) A group established by the ETSI in December 2012 after it had become the core of the world's telecommunication carriers. It promotes the study of carrier-driven network virtualization technology.
*5ETSI NFV ISG proof-of-concept framework
Certified as an ETSI proof of concept, this platform technology meets the reliability and scalability needs that service applications require.
Reference: http://www.ntt.co.jp/news2014/1405e/140501a.html
*6NTT DATA's traffic congestion predictions and traffic signal control simulations
Experiments to check the effects of alleviating traffic congestion in Jilin City, China
Reference: http://www.nttdata.com/jp/ja/news/release/2015/012303.html(japanese)
Information is current as of the date of issue of the individual press release.
Please be advised that information may be outdated after that point.
NTT STORY
WEB media that thinks about the future with NTT










