Microsoft ends support for Internet Explorer on June 16, 2022.
We recommend using one of the browsers listed below.
- Microsoft Edge(Latest version)
- Mozilla Firefox(Latest version)
- Google Chrome(Latest version)
- Apple Safari(Latest version)
Please contact your browser provider for download and installation instructions.
August 5, 2020
NTT Corporation
500 GHz Band, 20 dB Gain Amplifier IC Applicable to Terahertz Sensing
—Technology Expected to Improve Accuracy of Weather Forecasting for Extreme Events such as Typhoons and Torrential Rain—
NTT Corporation (Head Office: Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; President and CEO: Jun Sawada; hereinafter "NTT") has achieved a world's first in applying a neutralization circuit*1 to an amplifier circuit in the 500 GHz band by using an inductor component to neutralize the transistor's parasitic capacitance that limits amplifier frequency. With this technology, NTT has successfully achieved a 20 dB high-gain amplifier IC in the 500 GHz band.
The 500 GHz band is a high-frequency band known as terahertz waves*2 that is expected to have application to sensing and other fields. To use such a frequency band with frequencies higher than those of microwaves and millimeter waves, the development of a high-gain amplifier IC has been anticipated.
NTT has achieved a 500 GHz band amplifier IC applying original neutralization circuit technology using an InP*3-based HEMT*4 and has confirmed a power amplification factor (gain) of 20 dB, which is 2.5 times greater than currently reported gain in 500 GHz band amplifiers. This technology is therefore expected to help improve the accuracy of weather forecasting for extreme events such as typhoons and torrential rain. The plan is to present detailed information on this technology via the newly established Late News*5 system at IEEE International Microwave Symposium 2020 (IMS2020) to be held online on the Internet from August 4 United States time.
1. Background to Research
Terahertz waves that include the 500 GHz band constitute a frequency band that exhibits little interference with other systems or natural radiation. This band features electrical characteristics that enable accurate determination of water vapor, oxygen concentrations, etc., so applying it in addition to the frequencies (7 GHz - 80 GHz) currently being used in meteorological observations is expected to improve the accuracy of weather forecasting such as for typhoons and torrential rain.
2. Research Result
This research has achieved a 500 GHz band amplifier IC applying original neutralization circuit technology using an InP-HEMT and has successfully achieved a 20 dB high-gain amplifier IC. This is 2.5 times the gain reported so far for 500 GHz band amplifier ICs, which makes this a promising technology for improving the accuracy of weather forecasting especially for extreme events such as typhoons and torrential rain.
3. Future Development
This amplifier IC can perform signal amplification with a high gain of 20 dB in the 500 GHz band, which up to now has been difficult to achieve anywhere in the world. In this capacity, we expect it to find application in a variety of fields such as imaging and large-capacity wireless communications in addition to sensing. Going forward, the deepening of this technology will contribute to the advancement of science and technology that can make everyone's life safer and more secure, more prosperous, and more convenient while giving hope for the future of mankind.
4.Technical Points
An amplifier IC using an InP-HEMT having superior high-speed and high-gain characteristics has been achieved. In conventional amplifiers, the operating frequency has been held to about 60% of transistor performance (fMAX*6). Against this background, NTT proposed the neutralization circuit shown in Figure 1. This circuit uses an inductor component to neutralize the transistor's parasitic capacitance component, which is a factor limiting amplifier frequency. NTT constructed a prototype amplifier IC (Figure 2) applying this circuit technology to terahertz waves and successfully achieved amplifier operation with a gain of 20 dB in the 500 GHz band exceeding 80% of fMAX (Figure 3). This work was supported in part by the FY2018 - FY2020 "Research and Development of Basic Technology for Terahertz Sensing Systems" R&D program of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications.
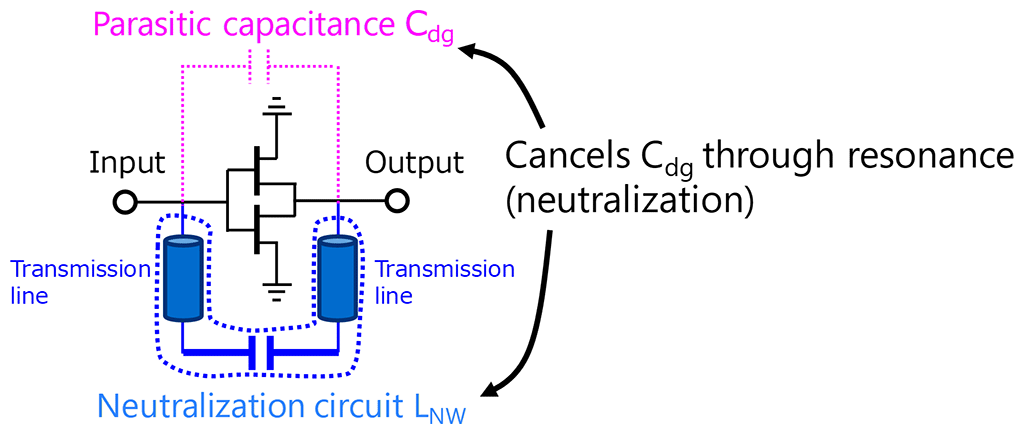 Figure 1 Neutralization circuit
Figure 1 Neutralization circuit
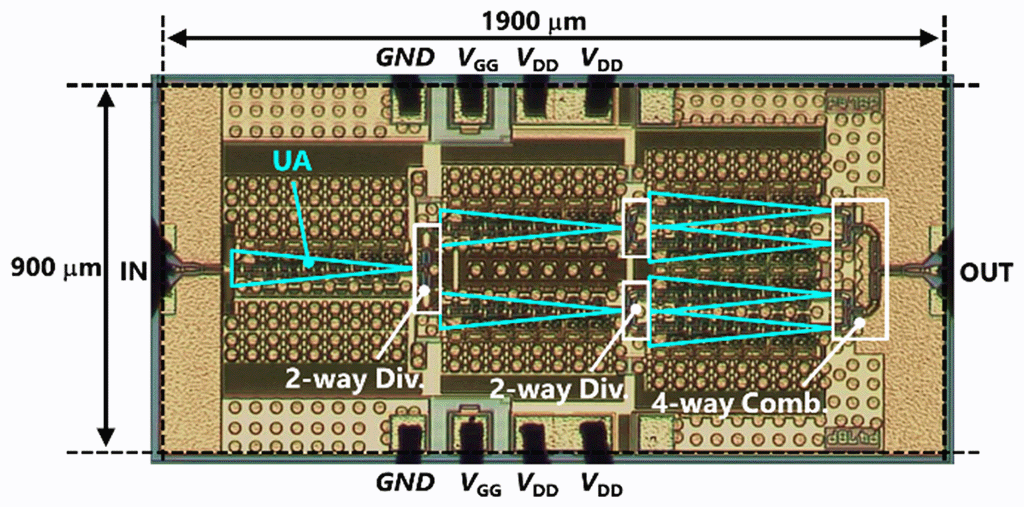 Figure 2 Prototype amplifier IC
Figure 2 Prototype amplifier IC
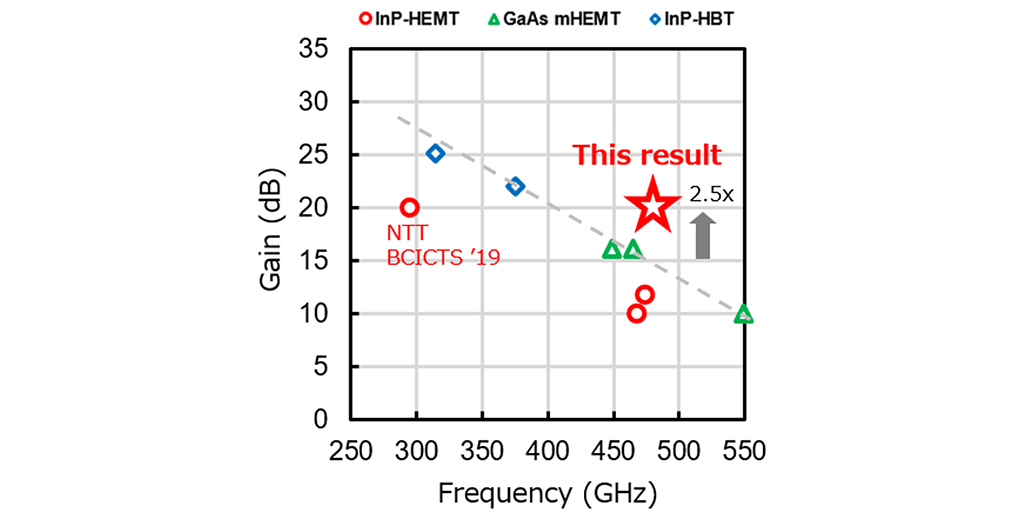 Figure 3 Ranking of this result (amplifier IC frequency vs. gain)
Figure 3 Ranking of this result (amplifier IC frequency vs. gain)
Glossary
- Neutralization circuit
A neutralization circuit removes (neutralizes) an unnecessary capacitance component that exists parasitically in a transistor (parasitic capacitance). The configuration of a neutralization circuit can take on various forms, such as canceling the parasitic capacitance by adding a signal with the same capacitance but reverse phase, or adding an inductor having opposite properties of that capacitance. - Terahertz waves
Just as the quantity 103 is called a "kilo (k)," 109 is called a "giga (G)" and 1012 a "tera (T)." "Hertz (Hz)" indicates the number of cycles that an alternating electric signal or electromagnetic wave goes through in one second. It is the unit of a physical quantity called "frequency." In short, one terahertz (1 THz = 1,000 GHz) is the frequency of an electromagnetic wave that cycles 1 × 1012 times per second. "Terahertz waves" often refer to electromagnetic waves in the frequency range from 0.3 THz to 3 THz. - InP
Indium phosphide. III-V group of compound semiconductors consisting of indium and phosphide. Used for achieving functions in applications requiring high-speed and high-output properties. - HEMT
High Electron Mobility Transistor - Late News
- International conferences sometimes use a system for selecting breakthrough achievements as a Late News Paper even if the deadline for submitting papers has already passed. Also called a Post Deadline Paper. Such a Late News system was established this year at the IMS international conference where this NTT achievement will be presented. A carefully screened paper that satisfies strict selection criteria beyond that of ordinary submitted papers can be selected as a Late News Paper.
- fMAX
The symbol fMAX refers to "maximum oscillation frequency." It is a figure of merit with respect to the high-frequency performance of a transistor and indicates the theoretical upper limit of frequency at which the transistor can amplify a signal. As transistor fMAX increases, signals of higher frequencies can be amplified.
Presentation plans
This achievement will be presented at International Microwave Symposium 2020 held online from August 4 under the title "475-GHz 20-dB-Gain InP-HEMT Power Amplifier Using Neutralized Common-Source Architecture" from 11:00 AM, August 5 local time.
| Technical Session: | Th2B: Late-breaking News from Terahertz Frontier |
|---|---|
| Time: | Can be viewed from 11:00 AM, August 5 local time |
| Title: | 475-GHz 20-dB-Gain InP-HEMT Power Amplifier Using Neutralized Common-Source Architecture |
| Conference Web site: | https://ims-ieee.org/ https://ims-ieee.org/technical-program/technical-sessions |
Contact point for inquiries from news organizations on this matter
■NTT Corporation
NTT Science and Core Technology Laboratory Group
Public Relations
Tel: 046-240-5157
E-mail: science_coretech-pr-ml@hco.ntt.co.jp
Information is current as of the date of issue of the individual press release.
Please be advised that information may be outdated after that point.
NTT STORY
WEB media that thinks about the future with NTT










