Microsoft ends support for Internet Explorer on June 16, 2022.
We recommend using one of the browsers listed below.
- Microsoft Edge(Latest version)
- Mozilla Firefox(Latest version)
- Google Chrome(Latest version)
- Apple Safari(Latest version)
Please contact your browser provider for download and installation instructions.
November 2, 2021
NTT Corporation
Unprecedented Optical Network Technologies to Support Esports
Achieving Breathtaking Gaming UX in Remote Esports Events
NTT Corporation (NTT) has achieved a world first in confirming that optical network technologies can well support remote esports*1 events. IOWN All-Photonics Network (APN)*2, which has the features of large capacity, extremely low latency, and no latency fluctuation, and APN User Terminal (prototype) enables the long-distance optical transport of HDMI/DisplayPort video signals and USB signals at signaling rates of 100 Gbps and beyond. In addition, the APN User Terminal offers precise network delay measurement and delay adjustment to ensure fairness in remote esports competitions. This technology offers unprecedented gaming UX in remote esports events among multiple cities.
This research will be demonstrated in the NTT R&D Forum on November 16 to 19, 2021. (*)
(*)Please see the following site for details on the NTT R&D Forum, which will be held from November 16th. http://www.rd.ntt/forum/
1. Background
Throughout the world, the popularity of esports related activities is growing, and they will spread further in the future. For example, there are professional level esports competitions, and the Olympic Virtual Series*3 held by the International Olympic Committee. There are also moves underway to make esports an official venue for various competitive events.
In addition, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, our lifestyles are dramatically changing. Even in esports, remote events between multiple locations are being held. Therefore, the importance of network technologies that can support remote events is rapidly increasing. (Figure 1)
Remote esports events currently use the Internet. However, its best effort nature creates significant issues with network latency and its fluctuation. Given this background, it is extremely difficult to achieve fairness between players, especially when the competitors are playing in different locations; it is impossible to hold professional level esports events on the Internet.
2. Technical Points
NTT are proposing the IOWN, which will create an innovative information infrastructure by 2030. The APN is one of IOWN's three pillars. APN will significantly improve the performance of future communications by using optical-based technologies.
A recent advance is our construction of an APN experimental environment, which can provide optical paths to accommodate user requests. The optical paths have the features of large capacity over 100 Gbps/lambda, extremely low latency fluctuation and absolute latency values approaching the physical limits. The APN experimental environment consists of Optical Processing Nodes, and APN Controller. The Optical Processing Nodes treat optical signals without electrical processing, and the APN Controller controls these nodes. We have prototyped APN User Terminals, that will be installed at user premises and provide paths of 100 Gbps or more to users. (Figure 2 / Technical Point 1)
The APN User Terminal can accommodate uncompressed or slightly-compressed HDMI/DisplayPort video signals and USB signals in the 100 Gbps and beyond optical signal. The optical signal can be transferred over 100 km, 1000 km or much more. These features enable users to use remote servers in distant data centers without local PC or gaming consoles. (Figure 2 / Technical Point 2)
In addition, the APN User Terminal has the functionalities of network delay measurement and delay adjustment with 1 microsecond accuracy. Network latency consists of two parts: optical transmission delay in the optical fiber, and processing delay in the communication equipment. The speed of light in optical fiber is 200,000 km/second, so it takes 5 milliseconds to traverse a 1000 km optical fiber. This delay is inevitable. On the other hand, with regard to processing delay, we are trying to decrease the processing delay by eliminating electrical processing-based equipment such as routers, layer 2 switches, and regenerative repeaters. We are also developing low latency signal processing to approach the physical limits. Given this situation, we can measure the delay of each communication path and adjust (add) any delay if necessary. This feature yields communication paths whose characteristics very well suit latency sensitive applications. (Figure 2 / Technical Point 3)
In APN, the APN controller manages multiple APN User Terminals, and in response to user requests, the APN Controller establishes end-to-end communication paths with appropriate quality by configuring the Optical Processing Nodes.
3. Application Examples
One suitable and attractive application is hosting esports events among multiple cities. Our network technologies offer an unprecedented gaming UX very similar to the UX of in-person events.
As one example, our network technologies enable an esports event to be established among four cities: Tokyo, Osaka, Sapporo and Fukuoka. Gaming video information (HDMI/DisplayPort) which is generated by a gaming server in a data center in Tokyo is transported to each player in Tokyo, Osaka, Sapporo and Fukuoka, and user's game operation information (USB) is transported from each city to the data center in Tokyo.
Depending on the distance between each city and the data center in Tokyo, there is difference in network delay. However, our delay measurement and delay adjustment functionalities can adjust each user's network delay so that they are the same value with 1 microsecond accuracy. This feature enables professional level remote esports events by offering fairness from the viewpoint of network delay. In addition, these network technologies also offer overwhelming experience in terms of live commentary and remote watching by connecting commentary and viewing sites.
4. Future Plans
We will challenge our network technologies by conducting field trials of esports events. Our unprecedented gaming UX will greatly enhance esports evolution in collaboration with esports and gaming industries. We are also considering the application of these network technologies to cloud-gaming by leveraging the APN features of large capacity and low latency. We are also targeting further improvements to the gaming UX by conducting research on not only network issues, but also server and software issues by collaborating with various industries.
Our network technologies can form a future network infrastructure that supports various post COVID-19 remote activities. We are applying our technologies to not only entertainment services including gaming, but also tele-work, education, arts, telemedicine, remote collaboration, amongst others, and we would like to push on towards the society based on the IOWN concept.
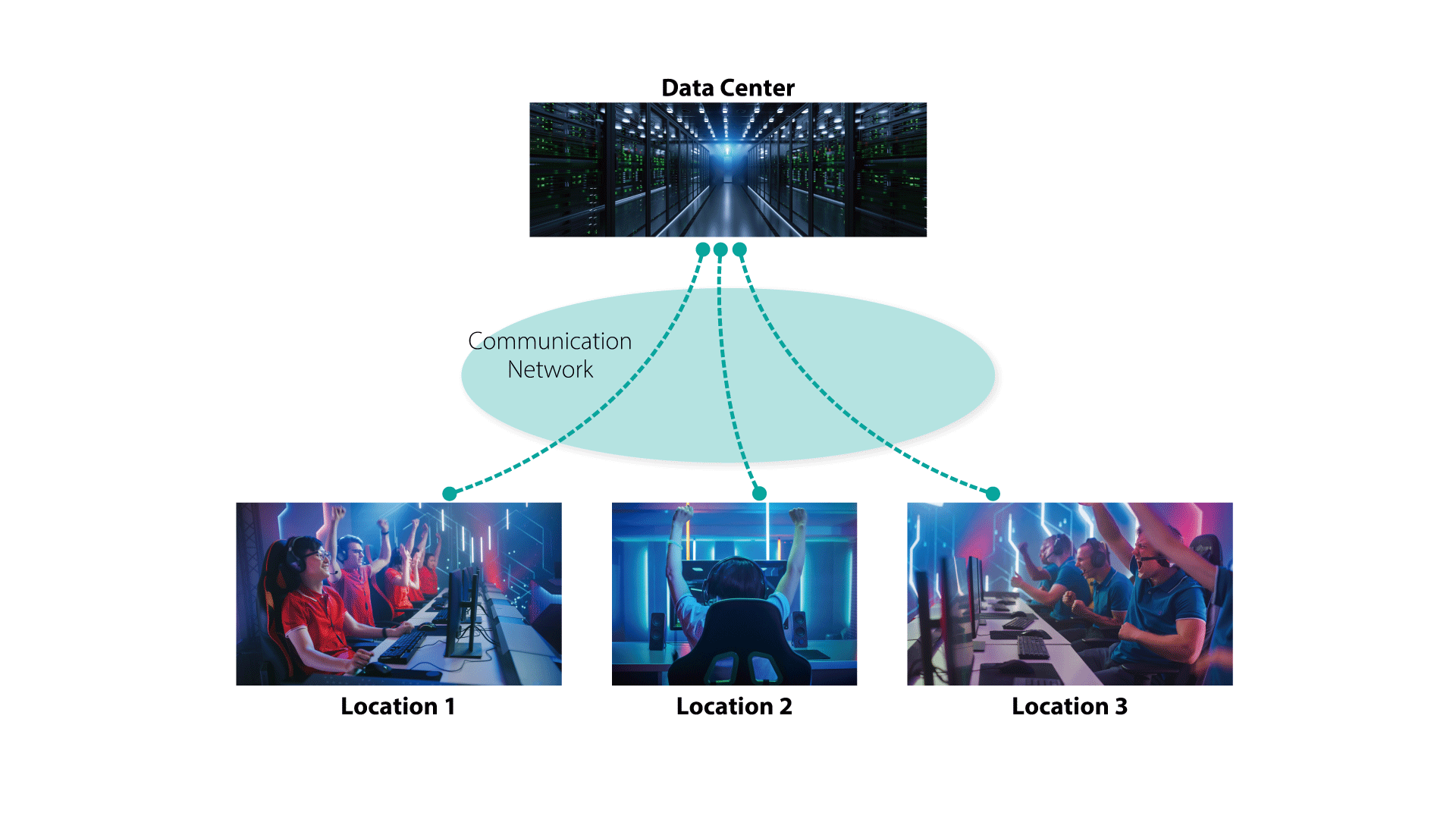 Figure 1: Widespread interest in remote esports events
Figure 1: Widespread interest in remote esports events
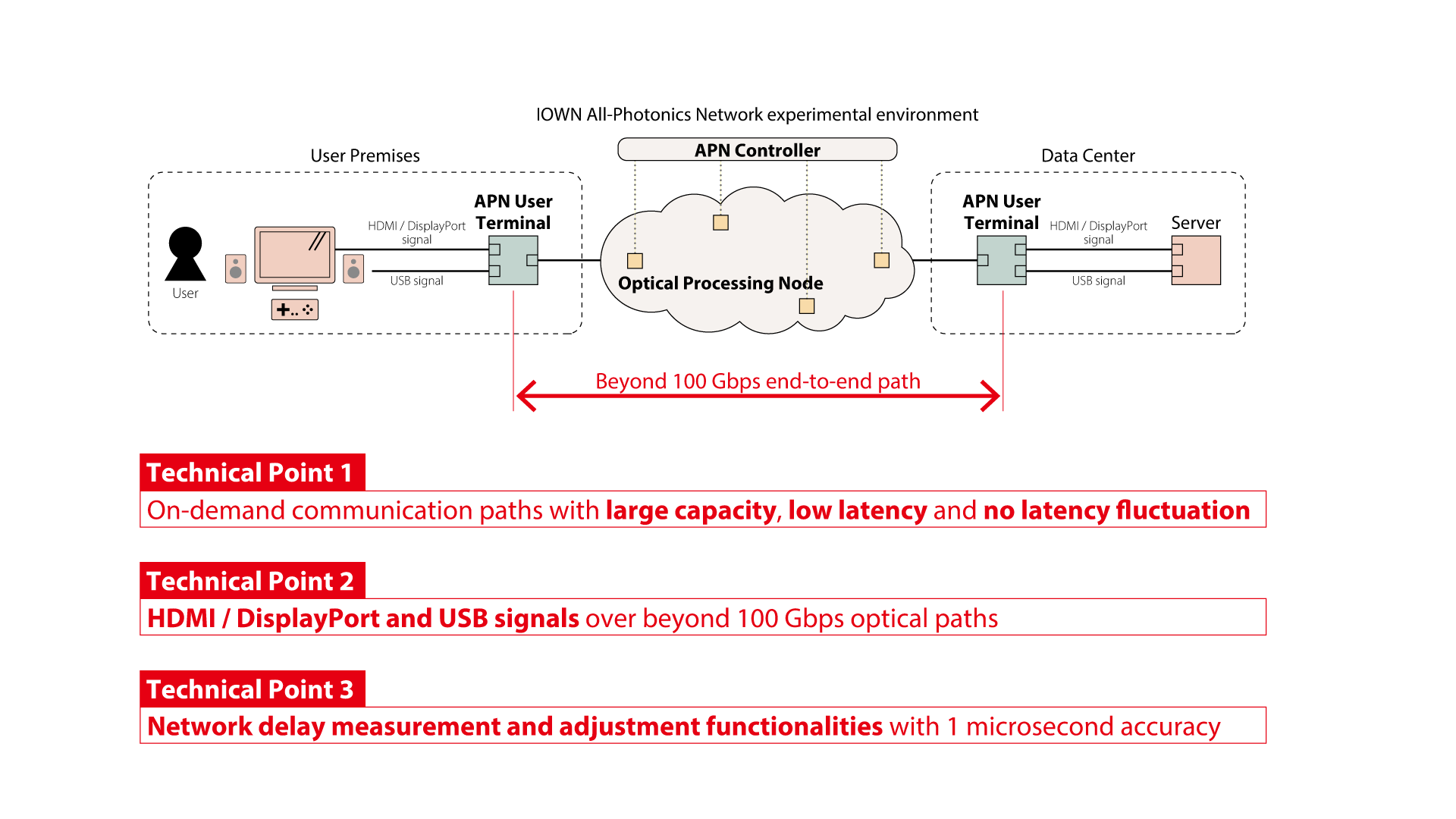 Figure 2: IOWN All-Photonics Network and APN User Terminal provide beyond 100 Gbps paths to users
Figure 2: IOWN All-Photonics Network and APN User Terminal provide beyond 100 Gbps paths to users
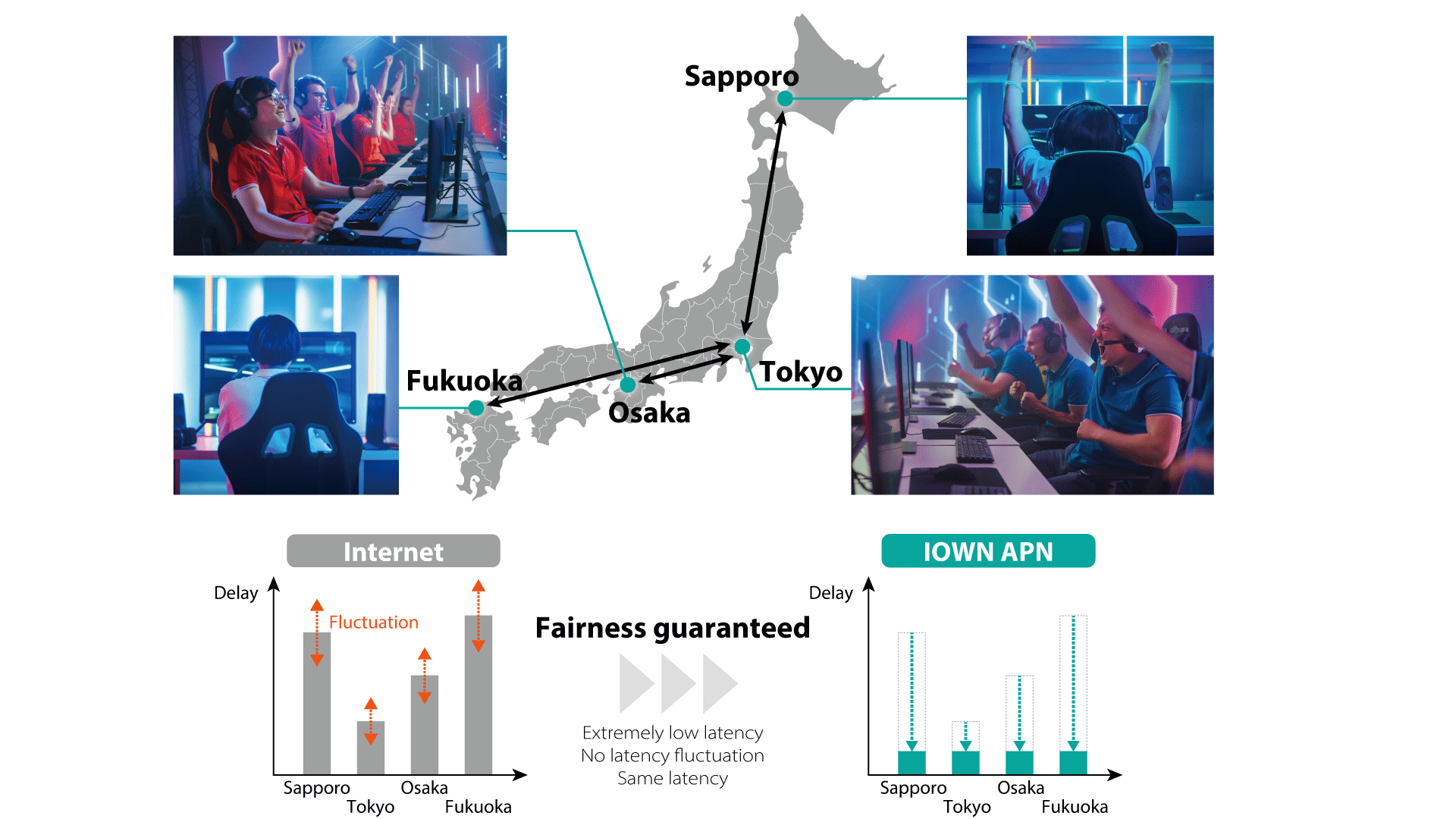 Figure 3: Application example of esports event in four cities: Tokyo, Osaka, Sapporo and Fukuoka
Figure 3: Application example of esports event in four cities: Tokyo, Osaka, Sapporo and Fukuoka
References
Glossary
*1esports
A form of competition using video games. Esports often takes the form of organized, multiplayer video game competitions, particularly between professional players, individually or as teams.
*2IOWN All-Photonics Network
IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network) comprises three main technology components: "allphotonics network (APN)" that uses optical processing on not only networks but also device processing; "digital twin computing" that enables high-speed, realtime interaction between things and people in cyberspace; and Cognitive Foundation®, in which these and various other ICT resources are efficiently managed.
APN incorporates new optical technologies at every level, from networks to devices, and even inside chips, to enable ultralow power consumption, ultrahigh speed processing that has not been possible until now.
By allocating different wavelengths to different functions in a single optical fiber, it becomes possible to provide multiple functions that support social infrastructure without mutual interference, including information communication functions such as internet and sensing functions.
*3Olympic Virtual Series
OVS (Olympic Virtual Series) is held by the International Olympic Committee (IOC) as a "new Olympic digital experience". The first finals of 5 types of games (baseball, cycling, rowing, sailing and motorsports) were held from May to June 2021.
For media inquiries regarding this matter, please contact
Public Relations Office
NTT Science and Core Technology Laboratory Group
science_coretech-pr-ml@hco.ntt.co.jp
Information is current as of the date of issue of the individual press release.
Please be advised that information may be outdated after that point.
NTT STORY
WEB media that thinks about the future with NTT










