Microsoft ends support for Internet Explorer on June 16, 2022.
We recommend using one of the browsers listed below.
- Microsoft Edge(Latest version)
- Mozilla Firefox(Latest version)
- Google Chrome(Latest version)
- Apple Safari(Latest version)
Please contact your browser provider for download and installation instructions.
February 20, 2023
NTT Develops World's First Ultra-Compact Baseband Amplifier IC Module with Built-in DC Block Function and 100GHz Bandwidth Performance
A Breakthrough Technology that Opens the Door to Next-generation, High-speed Communication and Measurement Applications
Tokyo - Feb. 23, 2023 - NTT Corporation (President and CEO: Akira Shimada, "NTT") has succeeded in developing an ultra-compact baseband amplifier IC module with an ultra-broadband performance of 100GHz. This technology is expected to be used in future all-photonics networks, namely IOWN and 6G, and fields achieving cutting-edge measurements since they will require an ultra-broadband signal amplification function4 rid of distortion
To achieve this breakthrough, NTT applied its InP-based heterojunction bipolar transistor (InP HBT) technology1to improve the performance of amplifier ICs and package mounting technology to incorporate a DC block function2 with 100 GHz bandwidth performance, realizing the world's first ultra-compact amplifier IC module. In addition, since NTT's development has a built-in DC block function and is ultra-compact, it can be directly connected to various devices, making it a highly usable module.
This result will enable ultra-high-speed optical communication in the next-generation IOWN network and cutting-edge measurement applications. Details of this technology were published online in IEEE Microwave and Wireless Technology Letters on (February) 16, 2023.
Research Background
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the digital transformation of various services, so online communication traffic is exploding. NTT's core optical network, IOWN, will require transmission speeds of more than 2 terabits per second and a baseband amplifier IC module that can amplify the signal. In addition, in the areas of experimentation and measurement that support such advanced research, there is already a need for ultra-broadband and compact electric amplifiers, and the demand is increasing.
To date, NTT has developed a prototype of an ultra-broadband baseband amplifier IC module with a 1mm coaxial connector and has conducted the world's first demonstration experiment of optical transmission exceeding 2 terabits per second5. However, previous prototype modules were large and required external DC block parts to connect to the front and rear devices.
Research Achievements
By increasing the performance of amplifier ICs using InP HBT technology and advancing package mounting technology, NTT succeeded in realizing the world's first ultra-compact amplifier IC module that achieves both ultra-wideband performance of 100 GHz and DC block function integration (Figure 1).
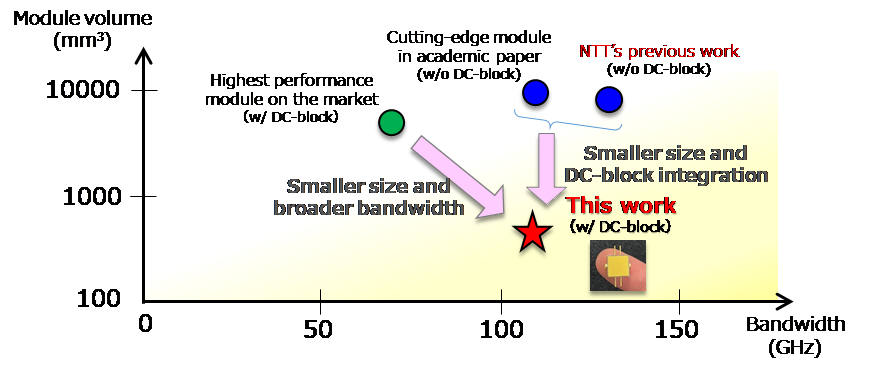 Fig. 1: Comparison of conventional technology and this result
Fig. 1: Comparison of conventional technology and this result
Ultra-broadband baseband amplifier IC based on InP HBT technology
NTT has achieved broad peaking characteristics (characteristics that emphasize gain on the high-frequency side) by further improving the performance of ultra-broadband baseband amplifier ICs6 using InP HBT technology developed by the company (Figure 2). This peaking characteristic makes it possible to compensate for high-frequency signal loss caused by package mounting and to ensure gain flatness (a characteristic in which a constant amplification factor is obtained from low frequencies to high frequencies) as an amplifier IC module.
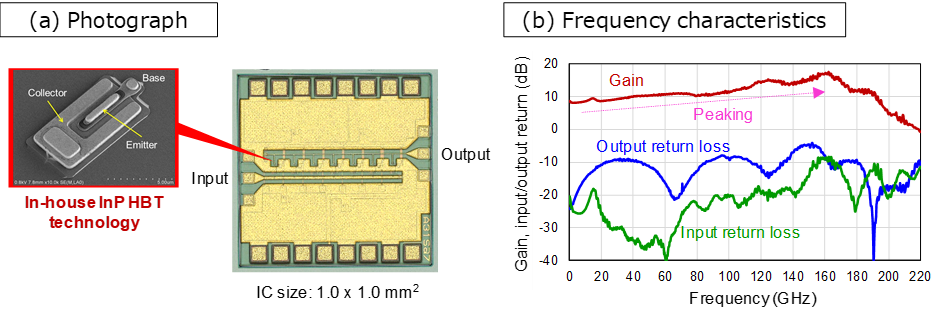 Fig. 2: Baseband amplifier IC using InP HBT technology (a) Photo (b) Frequency characteristics
Fig. 2: Baseband amplifier IC using InP HBT technology (a) Photo (b) Frequency characteristics
Ultra-broadband/ultra-small package mounting technology
NTT has ensured ultra-broadband characteristics by adopting a push-on type coaxial connector instead of the conventional thread-on type coaxial connector for the interface and devising the design of the joint between the coaxial and the internal high-frequency board. Also, researchers have achieved a drastic reduction in the size of the package. In addition, NTT made full use of precise high-frequency design technology to achieve DC block function integration (which was previously difficult to combine with ultra-wideband characteristics) by mounting a small thin-layer capacitor on the internal high-frequency substrate.
By combining these technologies, NTT achieved both ultra-broadband characteristics of 100 GHz or more and DC block function integration in an ultra-compact size with a volume ratio of less than one-tenth of conventional devices (Fig. 3). Finally, the researchers demonstrated that this amplifier IC module can amplify an ultra-wideband PAM-4 signal7 with a symbol rate8 of 112 gigabaud without distortion (Fig. 4).
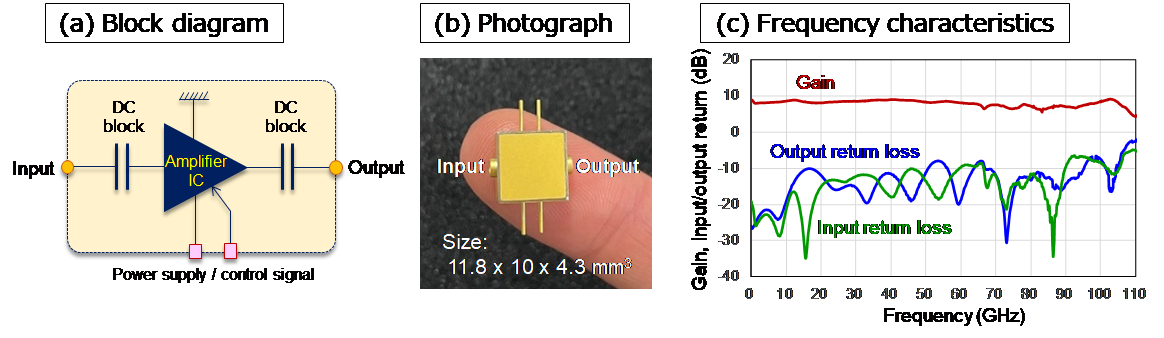 Fig. 3: Baseband amplifier IC module (a) Configuration block diagram (b) Photo (c) Frequency characteristics
Fig. 3: Baseband amplifier IC module (a) Configuration block diagram (b) Photo (c) Frequency characteristics
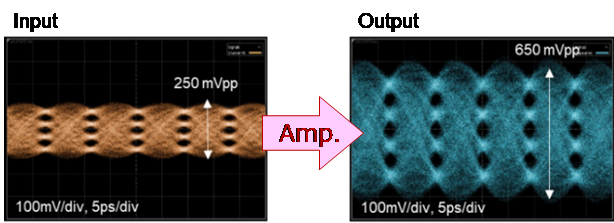 Fig. 4: Amplification experiment result of a 112 gigabaud PAM-4 signal generated by this amplifier IC module
Fig. 4: Amplification experiment result of a 112 gigabaud PAM-4 signal generated by this amplifier IC module
Future Development
This result will be put into practical use at an early stage in applications where the need for ultra-broadband signal amplification has already become apparent, such as next-generation, ultra-high-speed optical communications and cutting-edge experimental and measuring instrument applications that support the research and development of 6G.
In the medium term, NTT will further improve their IC and package mounting technology and study application for ultra-high-speed optical transceivers in the next-generation IOWN network.
1Heterojunction bipolar transistor using indium phosphide, a group III-V semiconductor. Transistor with excellent speed and withstand voltage.
2A function that removes the direct current (DC) component included in the signal. Essential to avoid device failures and malfunctions when connecting devices with different DC operating voltages.
3NTT R&D Website: "What's IOWN?" https://www.rd.ntt/e/iown/0001.html
4A signal of the information to be sent/received in communication. This baseband signal is carried on a carrier (carrier wave) and transmitted. A broadband for the baseband signal means that a large amount of information can be transmitted.
5NTT News Release: "NTT Achieves the World's Fastest Optical Transmission of over 2 Tbits/s Per Wavelength: A Large Capacity Communication Network Technology to Support IOWN & 6G"
https://group.ntt/en/newsrelease/2022/09/22/220922a.html
6NTT News Release: "NTT Achieves the World's Greatest Bandwidth of 241 GHz for an Amplifier IC: Enabling Ultra-High-Speed Device Technology for Next-Generation Data Centers and Beyond 5G"
https://group.ntt/jp/newsrelease/2019/06/03/190603b.html (Japanese only)
74-level Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) signal. A modulation method that can transmit 2-bit information per symbol by assigning 4-level signal states to 1 symbol.
8Represents the speed of modulation and indicates the number of modulations (waveform switching) per second. A 112 gigabaud signal means a signal with 112 billion modulations per second.
About NTT
NTT believes in resolving social issues through our business operations by applying technology for good. An innovative spirit has been part of our culture for over 150 years, making breakthroughs that enable a more naturally connected and sustainable world. NTT Research and Development shares insights, innovations and knowledge with NTT operating companies and partners to support new ideas and solutions. Around the world, our research laboratories focus on artificial intelligence, photonic networks, theoretical quantum physics, cryptography, health and medical informatics, smart data platforms and digital twin computing. As a top-five global technology and business solutions provider, our diverse teams deliver services to over 190 countries and regions. We serve over 75% of Fortune Global 100 companies and thousands of other clients and communities worldwide. For more information on NTT, visit https://www.rd.ntt/e/
###
NTT and the NTT logo are registered trademarks or trademarks of NIPPON TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CORPORATION and/or its affiliates. All other referenced product names are trademarks of their respective owners. © 2023 NIPPON TELEGRAPH AND TELEPHONE CORPORATION
Media Contact
Stephen Russell
Wireside Communications®
For NTT
+1-804-362-7484
srussell@wireside.com
Information is current as of the date of issue of the individual press release.
Please be advised that information may be outdated after that point.
NTT STORY
WEB media that thinks about the future with NTT