Microsoft ends support for Internet Explorer on June 16, 2022.
We recommend using one of the browsers listed below.
- Microsoft Edge(Latest version)
- Mozilla Firefox(Latest version)
- Google Chrome(Latest version)
- Apple Safari(Latest version)
Please contact your browser provider for download and installation instructions.
May 24, 2023
NTT Corporation
NTT Succeeded in Low Power Consumption of 5G Virtualized Radio Base Station (vRAN)
-- NTT's unique power-saving technologies were proved to reduce power consumption by up to 46% compared with conventional products --
NTT Corporation (Headquarters: Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, President & CEO: Akira Shimada, "NTT") demonstrated that power-saving enablers, technologies developed through NTT's research, can reduce power consumption of software-based virtualized base stations by up to 46% in an environment similar to an actual commercial network.
These power-saving enablers are planned to be incorporated into vendor's commercial virtualized base stations and be provided globally, contributing to the development of a sustainable society by helping telecommunications operators decarbonize.
1. Background
With the performance improvement of general-purpose CPUs and the evolution of softwarization and virtualization technologies for network functions, research and practical use of virtualized base stations have recently been attracting attention. Virtualized base stations are also called a virtual radio access network (vRAN), in which wireless base station functions are composed of software on a general-purpose server. Since virtualized base stations are deployed on general-purpose servers, they have the advantage of significantly reducing capital expenditure compared with dedicated hardware.
On the other hand, compared with dedicated hardware optimized for wireless base stations, general-purpose servers have inefficiencies associated with general-purpose processing. Thus, power consumption of virtualized base stations needs to be reduced. In general, there is a trade-off between performance improvement and power consumption reduction. Thus, achieving both in virtualized base stations is particularly difficult since base stations have microsecond-order latency requirements. Therefore, a solution to this problem has been sought.
2. Overview
NTT is researching and developing various technologies, including innovative technologies centered on optics, to realize the IOWN concept*1. As part of this effort, NTT is researching power-saving enablers that can be incorporated into software and achieve power saving. The power-saving enablers can be used in use cases with strict latency requirements.
2.1 Power saving enablers
The power-saving enablers are based on the concept of controlling software processing so that it is performed with the minimum computing resources required for a given workload, and they achieve a significant power-saving effect, especially at low loads. NTT started researching the power-saving enablers focusing on the aforementioned issue of reducing power consumption of virtualized base stations, analyzed each of their software process from a power consumption perspective, devised multiple technologies to improve inefficient processing, and demonstrated that the power-saving enablers can reduce power consumption of virtualized base stations without degradation performance. The software technologies of the power-saving enablers will enable greater power-saving effects by cooperating with "photonics-electronics convergence technologies," "all photonics network (APN)*2," and "super white box*3," which NTT is researching and developing to realize of the IOWN concept.
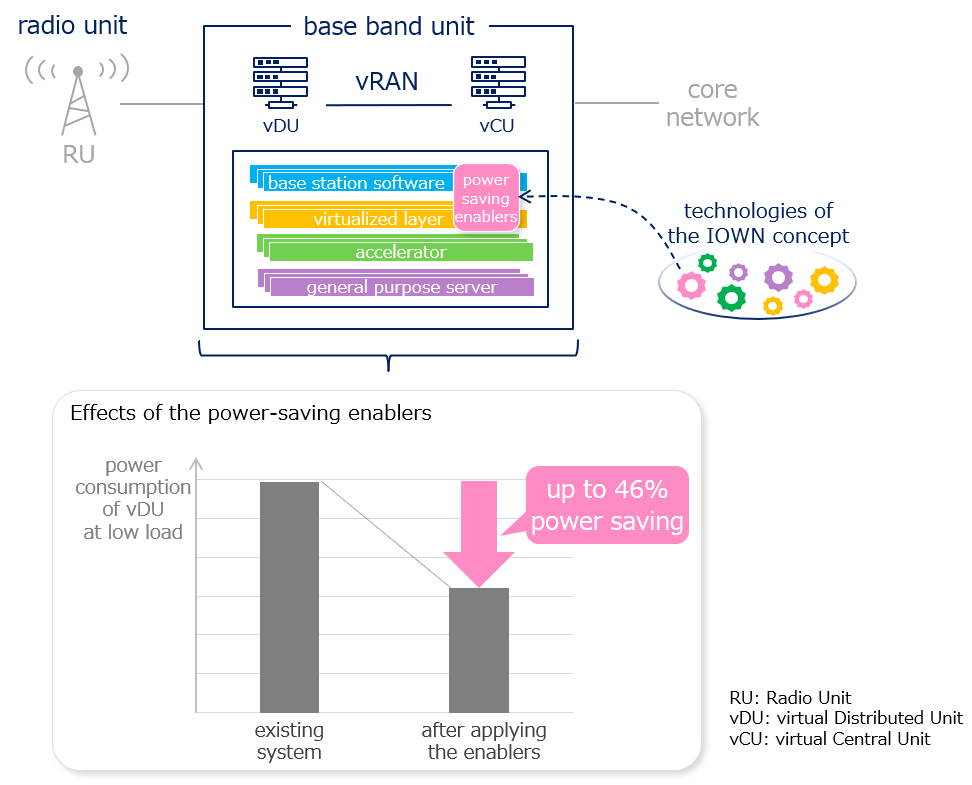 Figure 1: Overview of the power-saving enablers
Figure 1: Overview of the power-saving enablers
2.2 Technology demonstration experiment
For technology demonstration experiments, the power-saving enablers were incorporated into actual virtualized base stations provided by Fujitsu Limited to evaluate their effectiveness in an environment similar to an actual commercial network. As a first step, the effectiveness of the following power-saving enablers was demonstrated: (1) sleep-control technology of software processing under strict delay requirements, (2) flexible-scaling control technology of devices required for processing, and (3) control technology that maximizes power-saving functions of devices. These enablers were incorporated into products with two types of architecture (look-aside model*4 and in-line model*4), which are the mainstream in virtualized base stations. They were evaluated on a current general-purpose server and found to reduce power consumption by up to 46% under low traffic conditions.
3. Future plans
The power-saving enablers are planned to be licensed to vendors who need to utilize them. By globally providing these power-saving enablers through incorporating them into vendors' virtualized base stations, NTT will support decarbonization of telecommunications operators through power saving in 5G/6G networks, etc., with the aim of realizing a sustainable society. In addition, NTT will continue to research and develop power-saving technologies to realize the IOWN concept, thereby contributing to power saving across society as a whole.
Glossary
*1The IOWN Concept
The IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network) is an initiative for networks and information processing infrastructure including terminals that can provide high-speed, high-capacity communication utilizing innovative technology focused on optics, as well as tremendous computational resources.
https://www.rd.ntt/e/iown/index.html
*2All Photonics Network (APN)
APN achieves ultra-low power consumption and ultra-high speed processing, by introducing new optical technologies from the network to the terminals and chips. By allocating different wavelengths to different functions in a single optical fiber, it becomes possible to provide multiple functions that support social infrastructure without mutual interference, including information communication functions such as internet and sensing functions.
https://www.rd.ntt/e/iown/0002.html
*3Super White Box
With the aim of integrating networking and computing, etc., the super white box enables new computing with optical connectivity that breaks away from the traditional concept of servers, enabling reduced power consumption and low latency.
*4Look-aside model and in-line model
Highly parallel operations that general-purpose CPUs are not good at are often offloaded to accelerators such as graphics processing units (GPUs), field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), and application specific integrated circuits (ASICs). There are two types of architectures for offloading to accelerators: look-aside type architecture and in-line type architecture. In the case of vRAN, the former offloads parts of layer-1 radio signal processing, especially those with high processing load such as encryption and decryption, while the latter offloads all of layer-1 radio signal processing.
Media Contact
NTT IOWN Integrated Innovation Center
Planning Department, Public Relations Section
nttrd-pr@ml.ntt.com
Information is current as of the date of issue of the individual press release.
Please be advised that information may be outdated after that point.
NTT STORY
WEB media that thinks about the future with NTT










