Microsoft ends support for Internet Explorer on June 16, 2022.
We recommend using one of the browsers listed below.
- Microsoft Edge(Latest version)
- Mozilla Firefox(Latest version)
- Google Chrome(Latest version)
- Apple Safari(Latest version)
Please contact your browser provider for download and installation instructions.
April 5, 2024
NTT Corporation
Development of technology that computes similarity and correspondence between large-scale data at high speed and accuracy
Fast and accurate analysis of data relationships for more efficient generative AI and media processing
Tokyo - April 5, 2024 - NTT Corporation (NTT) has proposed a new fast algorithm for the optimal transport1, which seeks similarity and correspondence between input data, that obtains the optimal solution by utilizing cyclic symmetry2 latent in real-world data and has demonstrated its effectiveness theoretically and experimentally for the first time.
The proposed algorithm reduces the optimal transport problem to a small optimization problem with significantly fewer variables by utilizing cyclic symmetry and various optimization techniques and then solves the small optimization problem instead of the original problem. As a result, this algorithm obtains the optimal solution faster than solving the original optimal transport problem directly.
This will promote R&D to help people improve and transmit their visual cognitive abilities through comparison, quantification, and visualization of physical movements between experts and beginners, and advance toward the realization of service infrastructure to expand the abilities of a diverse range of people, including sports.
The results were presented at the 38th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence3 (AAAI-24, adoption rate 23.8%), the premier international conference in the field of AI, held in Vancouver, Canada, from February 20 to 27, 2024.
1. Background and overview of the study
As part of NTT's efforts to expand natural human abilities through ICT, we are conducting research to bring about innovative improvements in people's visual cognitive abilities by passing down superior visual perception (visual umwelt) by skilled people and AI who can identify essential changes and differences in the real world. Specifically, we aim to build a system for improving visual perception that detects only essential changes and differences accurately and visualizes them clearly through visual exaggeration. For example, we believe that it can help athletes learn motor skills by improving the visual perception of the top athlete's movements, help residents perform difficult surgery by improving the visual perception of the microtremor, and create an experience in which the intention of the athlete and performer is conveyed through visual exaggeration.
To realize the above system, basic technologies that detect changes and differences between large-scale data in the real world with high accuracy and high speed are required. In recent years, the optimal transportation problem has attracted attention as one of such technologies. However, solving the optimal transportation problem requires a huge computational cost. We have developed a technique to compute the similarity and correspondence between large-scale data based on the optimal transportation problem with high speed and accuracy by utilizing cyclic symmetry latent in real-world data, thereby reducing the computational cost.
 Figure 1 Real-World Images with Cyclic Symmetry (* Including Mirror Symmetry)
Figure 1 Real-World Images with Cyclic Symmetry (* Including Mirror Symmetry)
2. Technical points
- Use of cyclic symmetry latent in data
The proposed algorithm first divides the optimal transport problem into each symmetric component by utilizing the cyclic symmetry of input data, introduces a new auxiliary variable that contracts all symmetric components, and reduces the optimal transport problem to a small optimization problem with few variables. In this way, we reduced the computational cost by solving the small optimization problem instead of the original optimal transportation problem. - Process for reducing and reconstructing solutions of optimal transportation problems
While the conventional algorithm solves the optimal transportation problem directly, the proposed algorithm reduces the optimal transportation problem to another small optimization problem, solves it instead, and recovers the solution of the original optimal transportation problem (Figure 2). We have verified that the proposed algorithm obtains the optimal solution faster theoretically ad experimentally, even considering the two new processes of problem reduction and solution reconstruction (Figure 3). The most effective results are shown in Figure 3.
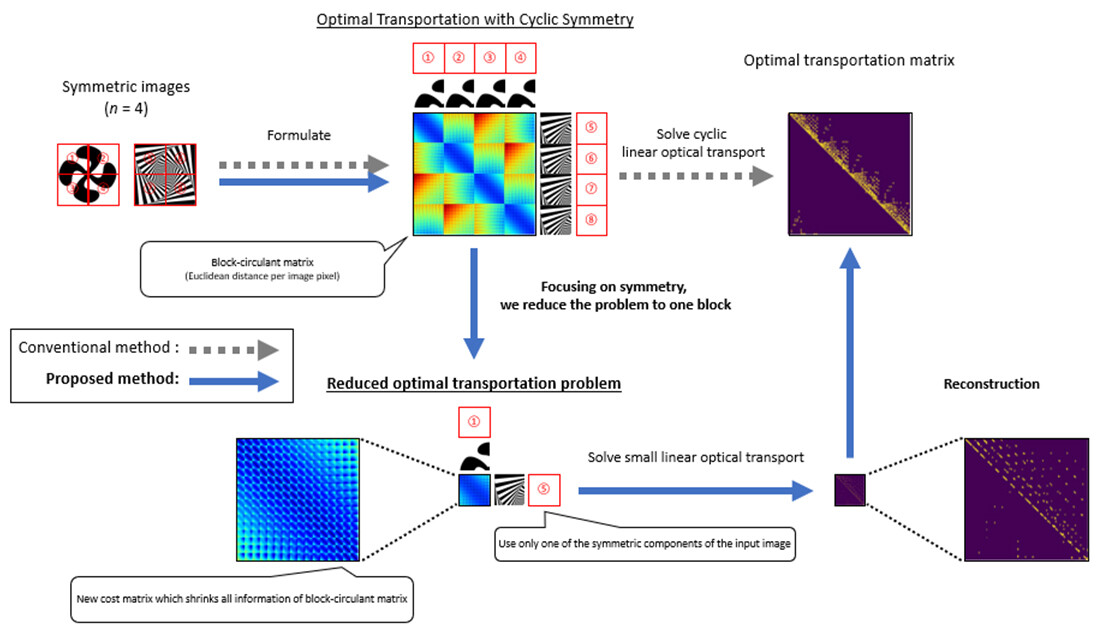 Figure 2 Overview of the Proposed Method
Figure 2 Overview of the Proposed Method
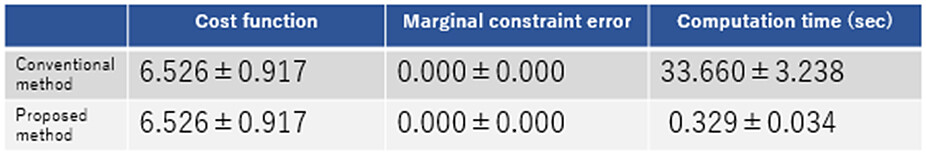 Figure 3 Experimental results when solving an optimal transport problem between 1000-dimensional data with (n=50)-order cyclic symmetry.
Figure 3 Experimental results when solving an optimal transport problem between 1000-dimensional data with (n=50)-order cyclic symmetry.
3. Outlook
We will continue to promote research and development for the improvement and transmission of people's visual and cognitive abilities through the comparison, quantification, and visualization of physical movements between experts and beginners using these results.
As one of the technological foundations of IOWN, which aims to connect diverse people around the world, and to build a service platform for expanding and demonstrating the capabilities of diverse people, including sports.
1Optimal transport
Refers to the problem of finding the optimal transportation plan between data that minimizes the total transportation cost. It was proposed by Monge in 1781 and formulated with linear programming by Kantorovich in 1942. Intuitively, as shown in Figure 4, this problem can be interpreted as a problem of finding a moving method (optimal transportation plan) that minimizes the total cost of moving sandpile 𝑝(𝑥) to sandpile 𝑞(𝑦).
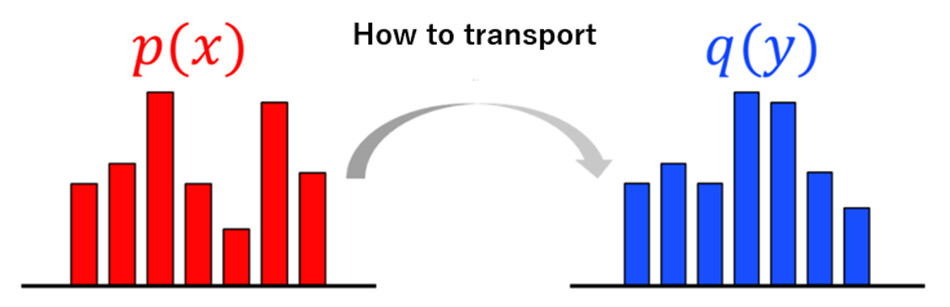 Figure 4 Examples of Intuitive Interpretations of Optimal Transportation Problems
Figure 4 Examples of Intuitive Interpretations of Optimal Transportation Problems
2Cyclic symmetry
A property in which the structure does not change after applying a transformation such as rotation or inversion (e.g., gears and snow crystals have cyclic symmetry).
3AAAI
Premier international conference on artificial intelligence
URL: https://aaai.org/aaai-conference/
About NTT
NTT contributes to a sustainable society through the power of innovation. We are a leading global technology company providing services to consumers and businesses as a mobile operator, infrastructure, networks, applications, and consulting provider. Our offerings include digital business consulting, managed application services, workplace and cloud solutions, data center and edge computing, all supported by our deep global industry expertise. We are over $97B in revenue and 330,000 employees, with $3.6B in annual R&D investments. Our operations span across 80+ countries and regions, allowing us to serve clients in over 190 of them. We serve over 75% of Fortune Global 100 companies, thousands of other enterprise and government clients and millions of consumers.
Media contact
NTT Service Innovation Laboratory Group
Public Relations
nttrd-pr@ml.ntt.com
Information is current as of the date of issue of the individual press release.
Please be advised that information may be outdated after that point.
NTT STORY
WEB media that thinks about the future with NTT










