Microsoft ends support for Internet Explorer on June 16, 2022.
We recommend using one of the browsers listed below.
- Microsoft Edge(Latest version)
- Mozilla Firefox(Latest version)
- Google Chrome(Latest version)
- Apple Safari(Latest version)
Please contact your browser provider for download and installation instructions.
August 7, 2025
HAZAMA ANDO CORPORATION
NTT, Inc.
HAZAMA ANDO and NTT Launch Key Initiative to Promote Remote and Automated Construction Work Control for Tunnels Using IOWN Technology
— Aiming to dramatically improve safety and productivity by defining use cases for remote construction work control over a distance of 1,000 km —
News Highlights:
- To move beyond conventional tunnel construction practices that are site-centric and reliant on skilled labor, efforts are underway to enable safe and efficient remote management from locations up to 1,000 km away using IOWN technology. To support this shift, four use cases have been defined to resolve key issues, along with the identification of priority operational areas that require focused efforts.
- The document approved by the IOWN Global Forum, the first of its kind in the construction industry, was made publicly available. Proof-of-Concept (PoC) testing is scheduled to begin by March 2026 to evaluate the effectiveness and feasibility of each use case.
TOKYO - August 7, 2025 - HAZAMA ANDO CORPORATION (Headquarters: Minato, Tokyo; Representative Director and President: Kazuhiko Kuniya; hereinafter referred to as "HAZAMA ANDO") and NTT, Inc. (Headquarters: Chiyoda, Tokyo; President and CEO: Akira Shimada; hereinafter referred to as "NTT") are leading efforts to develop use cases for IOWN technology to support the digital transformation of construction sites. As part of this initiative, the two companies, in collaboration with members of the IOWN Global Forum1, have formulated key operational areas and use cases for promoting remote and automated construction work control at tunnel construction sites. These efforts have been compiled into a document titled Use Case and Technology Evaluation Criteria - Construction Site2, which includes evaluation criteria for each use case. The document has been officially approved by the IOWN Global Forum and is now publicly available. This document primarily targets mountain tunnels.
Following the publication of this document, the team will seek broad participation from industry partners and plans to begin PoC testing by March 2026. Through this process, they will evaluate the effectiveness and feasibility of each use case and work toward establishing Reference Implementation Models that summarize the concepts and technical checkpoints necessary for system design and development.
This initiative aims to accelerate the creation of IOWN solutions that simultaneously improve safety and productivity both during tunnel construction and while tunnels are in service. It also seeks to build a next-generation ICT infrastructure that can be applied to tunnel construction sites in Japan and internationally.
Background and Overview
The construction industry continues to face numerous challenges, including a declining working-age population and an aging workforce, while also anticipating increased construction demand due to more frequent and severe natural disasters and the deterioration of aging infrastructure. In response, Japan's Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) formulated i-Construction 2.03 in 2024, aiming to drive industry-wide productivity improvements through automation of construction sites.
Tunnel construction sites, in particular, involve hazardous working environments and a decreasing number of experienced workers. As such, efforts are underway to implement data-driven prediction of collapses and accidents, as well as remote construction work control and remote inspection that allow offices and other off-site locations to monitor and inspect tunnel sites. Accurate, real-time understanding and analysis of on-site conditions requires high-capacity, low-latency communications, as well as robust data processing capabilities to support advanced AI-based analysis that leverages both current and historical construction site data across multiple locations such as construction sites, offices, and data centers.
However, at tunnel construction sites, investment in communication infrastructure has been limited due to the temporary nature of such systems, which are used only during the construction period. In addition, the traditional use of communications technology has been limited to surveying and tunnel face monitoring via cameras. As a result, network-based ICT infrastructure has yet to be widely adopted, posing a significant barrier to the implementation of digital solutions. After construction is complete and the tunnel is in service, regular inspections are required to ensure structural soundness. Yet with more than 10,000 tunnels across Japan, the shortage of qualified inspectors has become another critical issue.
To address these challenges, HAZAMA ANDO and NTT have worked with partner members under the IOWN Global Forum to explore the application of IOWN technology for achieving automation in tunnel construction. To promote system development for remote and automated construction work control, the team identified priority operational areas based on current issues in tunnel construction and defined four use cases expected to be feasible in the near term. These use cases assume a network configuration in which constructors, clients, construction sites, and data centers, located up to 1,000 km apart, are interconnected via IOWN APN4.
The resulting document outlining these early-stage use cases has become the first to be officially approved by the IOWN Global Forum within the construction industry and has been made publicly available.
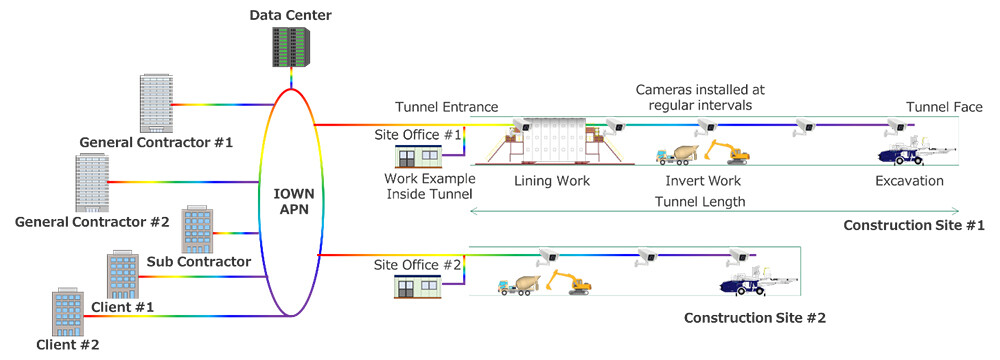 Figure 1 Conceptual Diagram of IOWN APN Implementation in Tunnel Construction Sites
Figure 1 Conceptual Diagram of IOWN APN Implementation in Tunnel Construction Sites
Overview of Use Cases for Transforming Construction Sites
As part of efforts to enhance productivity and safety in tunnel construction, four use cases expected to be achievable in the near term have been defined and compiled in the document Use Case and Technology Evaluation Criteria - Construction Site. This document is available for download from the IOWN Global Forum website at the following URL: https://iowngf.org/use-case-and-technology-evaluation-criteria-construction-site/
The document presents four early-stage use cases applicable to an environment in which construction sites, constructors' and clients' offices, and data centers are connected via IOWN APN. It also outlines the criteria required for their implementation. Below is a summary of each use case, along with the key challenges faced at construction sites. In the context of use cases, the distance between the constructor's office and the construction site is set to be 1,000 km.
■Use Case 1: Continuous Surveillance and Data Acquisition (Remote Monitoring):
| Current Issues and Challenges | Currently, most safety inspections rely on visual checks by experts, making it difficult to detect every change occurring at the construction site. In multiple construction sites where occupational accidents have occurred due to insufficient safety confirmation, there is a growing need for infrastructure that can detect site changes without relying solely on human observation. |
|---|---|
| Applicable IOWN Technology | - Real-time data transmission enabled by IOWN APN's high-capacity, low-latency communication |
| Expected Outcome | High-resolution video and sensor data from the construction site will be transmitted to remote locations via IOWN APN. This will enable continuous monitoring and early detection of safety risks through automated AI analysis. |
■Use Case 2: Event-Driven Monitoring and Data Analysis (Remote Analysis):
| Current Issues and Challenges | Currently, verification of whether the excavated shape conforms to design specifications is carried out manually at the tunnel face (excavation face), which is a hazardous area and requires considerable time. To balance construction progress and safety, there is a need for a system that minimizes downtime during inspections and surveying conducted by skilled workers in the tunnel face area. |
|---|---|
| Applicable IOWN Technology | - Utilization of remote computing resources through IOWN APN's high-capacity, low-latency communication - On-demand switching of IOWN APN connections based on measurement methods, enabled by flexible optical path5 configuration |
| Expected Outcome | By connecting the construction site with a remote processing environment via IOWN APN, the time required for analyzing large-scale point cloud data can be reduced to 60 seconds, without interrupting construction progress. This enables real-time decision-making regarding safety and quality. |
■Use Case 3: Mobile Inspection (Remote Inspection):
| Current Issues and Challenges | Some inspections required under management standards are already being conducted through remote inspection. However, current remote inspection methods face concerns such as low video resolution and latency-induced delays that may result in missed observations or instructions. To improve accuracy, a system is needed that enables inspectors to reliably assess key areas of concern, such as rock mass fractures and spring water, through enhanced image resolution and reduced communication delays. |
|---|---|
| Applicable IOWN Technology | - High-resolution remote inspection enabled by IOWN APN's high-capacity, low-latency communication - On-demand connection from non-permanently connected locations using flexible IOWN APN optical path configuration |
| Expected Outcome | By combining portable high-definition cameras with IOWN APN, inspectors at remote sites will be able to perform pinpoint inspections, accurately focusing on areas of interest as needed. |
■Use Case 4: Remote Maintenance Leveraging Embedded Infrastructure:
| Current Issues and Challenges | During the in-service phase (after construction is completed), regular inspections are conducted6. However, it is difficult to detect abnormalities that arise between scheduled inspections, and in some cases, urgent action is required by the time an issue is discovered. A monitoring system is needed to detect signs of structural issues early without increasing the burden on inspectors or affecting tunnel users, thereby enabling planned maintenance based on structural soundness. |
|---|---|
| Applicable IOWN Technology | - Repurposing of optical fiber installed during construction for sensing and data monitoring |
| Expected Outcome | By using optical fibers embedded during construction for sensing, the system enables remote, continuous monitoring of strain and acceleration along arbitrary points in the tunnel's longitudinal direction. This allows for the early detection of defects such as stripping, deformation, and aging deterioration. |
These early-stage use cases are expected to deliver the following benefits to stakeholders involved in construction projects.
| Stakeholders | Expected Benefits |
|---|---|
| General Contractor | - Remote Monitoring: Enables data-driven, traceable construction work control through real-time data collection, analysis, evaluation, and feedback from the site - Remote Analysis: Enhances risk prediction related to safety and quality, allowing safe and high-quality project execution within limited timeframes - Remote Inspection: Facilitates collaboration among contractors, clients, and other stakeholders regardless of physical distance |
| Subcontractors | - Remote Monitoring: Improves on-site safety by enabling early detection of potentially hazardous actions - Remote Analysis: Strengthens safety risk prediction to support safer working environments |
| Clients | - Remote Inspection: Enables efficient inspections regardless of the physical distance between clients and construction sites or contractors - Monitoring: Enhances post-construction maintenance and management through the use of network infrastructure developed during construction |
| Equipment and Service Providers | The network infrastructure established at construction sites and connectivity to data centers via IOWN APN provide opportunities to deliver new solutions, expanding the market for tunnel construction applications. |
Roles of Each Company
HAZAMA ANDO:
Under its "DX Vision 2030," HAZAMA ANDO became the first company in the construction industry to join the IOWN Global Forum in July 2022. Since then, it has played a leading role in driving the development of use cases and compiling related documentation for the industry. As part of its efforts to enhance productivity and safety in tunnel construction, HAZAMA ANDO will apply IOWN technology as the communications infrastructure for its internally developed i-NATM®, which is a mountain tunnel data integration platform.
NTT:
NTT has a proven track record in providing customers with high-speed, low-latency networks and is actively promoting the IOWN initiative, including the development of IOWN APN. In future discussions, NTT will explore and validate the architecture and specifications required for construction site use cases, focusing on new connection methods that enable on-demand access through flexible switching of optical paths within the APN and other IOWN components. NTT also plans to examine the future use and implementation of its proprietary technologies, including AI-based image and video analysis for efficient maintenance of infrastructure facilities developed by its research laboratories.
Future Outlook
Moving forward, HAZAMA ANDO and NTT will work toward the publication of Reference Implementation Models that provide the necessary information for system development. This will involve defining clear implementation requirements through ongoing discussions of architecture and evaluation criteria to accelerate solution development for each use case.
Each use case is scheduled to enter the PoC phase by March 2026, in collaboration with IOWN Global Forum members and partners. During the PoC phase, technical specifications related to communications will be examined through desk-based analysis, PC-based simulations, and lab-based experiments to verify network performance. Construction site testing using IOWN technology will also be conducted. The insights and results obtained through the PoC will be incorporated into future documentation, with the aim of building a next-generation ICT infrastructure that benefits a wide range of stakeholders involved in tunnel construction.
Furthermore, by leveraging HAZAMA ANDO's overseas construction experience and NTT's global presence, and working together with other IOWN Global Forum members, the companies aim to drive digital transformation across the construction industry both in Japan and internationally. Through continued integration of innovative technologies, they will help shape the future of construction and lead the way in redefining what construction sites can be.
1IOWN Global Forum
The objective of the IOWN Global Forum is to accelerate innovation and adoption of a communication infrastructure to meet our future data and computing requirements through the development of new technologies, frameworks, specifications, and reference designs in areas such as photonics R&D, distributed computing, use cases, and best practices. For more information, visit:
https://iowngf.org/
2Use Case and Technology Evaluation Criteria - Construction Site
This document, published by the IOWN Global Forum, presents specific use cases for particular industries and organizes the technical requirements and evaluation criteria necessary to realize them.
3i-Construction 2.0
https://www.mlit.go.jp/report/press/kanbo08_hh_001085.html(Japanese)
4IOWN APN (All-Photonics Network)
The IOWN APN is the communications infrastructure of the future. It is a high-quality all-optical network that responds to increasingly diverse and complex needs by making use of photonics-based technologies in all areas from network to terminal. This approach enables a variety of benefits including power saving, larger capacity networks and ultra-low delay on the order of a 100X improvement over traditional networks. For more details, visit:
https://www.rd.ntt/e/iown/
https://iowngf.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/IOWN-GF-RD-Open_APN_Functional_Architecture-2.0.pdf
5Optical path
An optical path refers to the route through which an optical signal travels from the transmitter to the receiver. Each optical path consists of a route formed by the optical fibers and optical node systems it passes through, along with specifications such as the capacity of the optical signal and the allocated wavelength. For more information about on-demand optical paths, visit:
https://group.ntt/en/newsrelease/2025/04/25/250425a.html
6For road tunnels, regular inspections are generally conducted every five years in accordance with the Guidelines for Periodic Inspection of Road Tunnels issued by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism.
https://www.mlit.go.jp/road/sisaku/yobohozen/yobohozen.html(Japanese)
"i-Construction2.0" is a registered trademark of the National Institute for Land and Infrastructure Management, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism.
"i-NATM" is a registered trademark of HAZAMA ANDO CORPORATION.
About HAZAMA ANDO
Hazama Ando is a corporate group that supports society through construction projects and operates in various locations around the world. In the civil engineering sector, it is responsible for the development of social infrastructure, including transportation networks such as roads and railways, lifelines such as water supply and sewage systems, and energy facilities, responding to societal needs through maintenance and upgrades. In the building sector, it supports customers throughout the entire lifecycle of buildings, from planning and design to construction, maintenance, and renewal, providing optimal buildings and services. Through manufacturing, it aims to realize a rich society where people can live comfortably and securely, proud of the future, and strives to be a corporate group that grows together with society.
About NTT
NTT contributes to a sustainable society through the power of innovation. We are a leading global technology company providing services to consumers and businesses as a mobile operator, infrastructure, networks, applications, and consulting provider. Our offerings include digital business consulting, managed application services, workplace and cloud solutions, data center and edge computing, all supported by our deep global industry expertise. We are over $90B in revenue and 340,000 employees, with $3B in annual R&D investments. Our operations span across 80+ countries and regions, allowing us to serve clients in over 190 of them. We serve over 75% of Fortune Global 100 companies, thousands of other enterprise and government clients and millions of consumers.
Media contacts
HAZAMA ANDO CORPORATION
Corporate Communication Department, Public Relations Group
Inquiry Form
NTT, Inc.
NTT IOWN Integrated Innovation Center
Public Relations
Inquiry Form
Information is current as of the date of issue of the individual press release.
Please be advised that information may be outdated after that point.
NTT STORY
WEB media that thinks about the future with NTT










