Microsoft ends support for Internet Explorer on June 16, 2022.
We recommend using one of the browsers listed below.
- Microsoft Edge(Latest version)
- Mozilla Firefox(Latest version)
- Google Chrome(Latest version)
- Apple Safari(Latest version)
Please contact your browser provider for download and installation instructions.
November 7, 2025
NTT, Inc.
World's First Demonstration of a Method for Detecting Early Signs of Road Cave-ins Using Reflected Radio Waves from SAR Satellites
~Enabling efficient and cost-effective identification of potential road cave-in risks without on-site work~
News Highlights:
- We have successfully demonstrated a method for detecting early signs of road cave-ins by analyzing data from Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) satellites1. This approach makes it possible to directly identify potential cave-in risks using only the radio wave data collected by orbiting SAR satellites.
- The method allows narrowing down areas with high road cave-in risk without any on-site inspection work.
- We will continue to enhance the reliability of this technology through demonstration experiments in collaboration with local governments.
TOKYO - November 7, 2025 - NTT, Inc. (Headquarters: Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; President and CEO: Akira Shimada; hereinafter "NTT") has achieved the world's first successful demonstration of a method to detect early signs of road cave-ins using data from SAR satellites. This method enables the efficient and cost-effective identification of high-risk locations without on-site operations.
The technology works by detecting early cave-in signs based on the scattering2 of radio waves with multiple polarizations3. The reliability of this technology has been verified through comparison with actual road cavity inspection data.
Building on this achievement, we will further improve the technology's reliability through demonstration experiments conducted in collaboration with local governments, contributing to greater safety and security in society. Under the "NTT C894" brand, we will continue to leverage satellites to address various challenges related to social infrastructure.
The research results will be exhibited at NTT R&D FORUM 2025 IOWN ∴Quantum Leap5 to be held from November 19 to 26, 2025.
 Figure 1 Overview
Figure 1 Overview
Background
In recent years, the deterioration of social infrastructure has progressed, and road cave-in incidents have become a societal concern. Meanwhile, municipalities responsible for managing social infrastructure have limited budgets and personnel, making it difficult to thoroughly maintain and inspect the vast infrastructure network spread across the country.
Currently, on-site visual inspections of underground structures such as sewer systems, which can cause cave-ins, as well as ground-penetrating radar surveys from the surface, are conducted. However, these methods cover only limited areas and require substantial labor and cost, making it impractical to inspect wide areas comprehensively. In addition, cave-ins caused by underground structures begin with cavity formation and progression below the surface. Satellite-based observations have largely been limited to surface conditions, which has posed challenges for applying satellite data to road cave-in detection.
NTT has also been researching satellite-based methods for estimating soil moisture content to support landslide prediction. The research has demonstrated that radio waves penetrate the soil and that soil moisture content can be estimated with high accuracy by analyzing the degree of wave penetration6.
Research Results
Against this backdrop, NTT has demonstrated a method for detecting early signs of road cave-ins using SAR satellites, which utilize radio waves capable of penetrating asphalt. By analyzing multiple polarizations, the method captures signs of potential cave-ins. Prior to a cave-in, the following conditions occur: (i) formation of underground cavities, (ii) ground disturbance, and (iii) surface unevenness (Figure 1). By analyzing the direction and intensity of the radio waves, the method can measure conditions (i) to (iii) (Figure 2). Additionally, by analyzing differences between satellite data collected at two different times, the progression of these conditions (i) to (iii) can be assessed.
Through this approach, we have established a method that can directly detect early signs of road cave-ins using radio wave measurements. Verification based on comparison with inspection data of underground cavities confirmed that these cavities can be identified using satellite data alone. Traditionally, vehicle-mounted ground-penetrating radar has been used to identify underground cavities, but applying this new technology is expected to reduce costs by approximately 85 percent.
The optical fiber-based ground monitoring method7, previously announced by NTT, is a technology that monitors the progression of underground cavities deep below the surface using underground optical fibers. This method enables early detection of major cavities that may lead to road cave-ins. In contrast, the new technology utilizes satellite-based radio waves and is therefore suited for detecting cavities that form closer to the surface. By using wide-area satellite data, it becomes possible to detect high-risk cavities that have advanced near the surface. Through the complementary use of these technologies, NTT aims to more reliably detect early signs of road cave-ins.
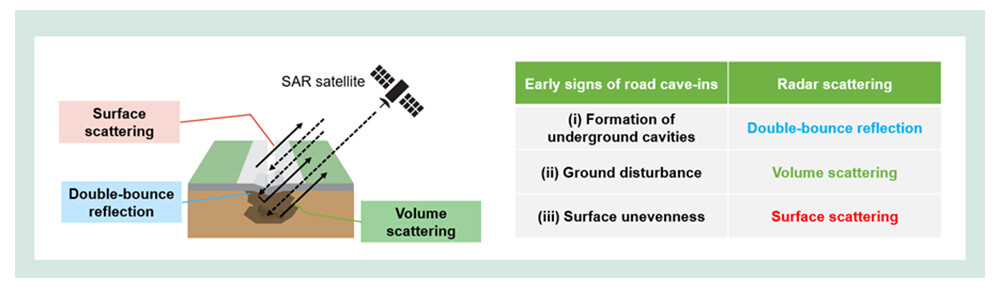 Figure 2 Relationship between scattering captured by satellite data and early signs of road cave-ins
Figure 2 Relationship between scattering captured by satellite data and early signs of road cave-ins
Key Technical Features
■ Identification of high-risk areas using satellite data alone and capability for regular monitoring
This technology does not indirectly estimate potential road cave-ins by combining data from underground utilities, environmental data, and satellite data. Instead, it directly measures conditions using radio waves from SAR satellites. As a result, early signs of road cave-ins can be detected with high reliability using only satellite data obtained from satellites orbiting and observing the Earth.
The mechanisms that lead to road cave-ins are complex, and deterioration can progress suddenly, making periodic inspections conducted every few years insufficient and prone to oversight. In contrast, SAR satellites regularly orbit the Earth, making it easier to monitor conditions more frequently than traditional on-site inspections. Continuous monitoring of road conditions through this technology reduces the risk of overlooking major cavity development.
■ Analysis of signal components derived from transmitted and received radio waves
When radio waves transmitted by SAR satellites interact with the ground, they may be reflected directly back (specular reflection) or scattered in various directions depending on the surface and subsurface conditions. By analyzing the polarization components of the radio waves in transmission and reception, the three scattering components shown in Figure 2 can be identified. By focusing on the process of road cave-in formation and the associated scattering components, this technology has successfully enabled road cave-in detection.
Future Developments
We will work with business partners and local governments to streamline and reduce the cost of inspection operations for preventing road cave-ins. Through demonstration experiments, we aim to further enhance the reliability of this technology. While listening to the needs and challenges faced by municipalities, we will continue developing this method so it can be practically implemented in the field.
By deploying sustainable maintenance technologies to address critical issues such as infrastructure deterioration and demographic aging, we will contribute to building a safer and more resilient society.
[Glossary]
1Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Satellite
A satellite equipped with radar that emits radio waves toward the Earth's surface and analyzes the returning signals to generate images. SAR satellites can observe regardless of weather or time of day and are used to assess disaster conditions and monitor forests and farmland.
2Polarization
The orientation of the oscillation of radio waves. As radio waves propagate, the direction in which they oscillate is defined as polarization. For example, waves oscillating vertically relative to the ground surface are called vertical polarization, while those oscillating horizontally are called horizontal polarization. This technology leverages these differences to detect characteristics of both the surface and subsurface of roads.
3Scattering
A phenomenon in which radio waves hit an object and return after being reflected in various directions. SAR satellites generate images by analyzing the intensity of these scattered signals.
4NTT C89
A brand name for space-related businesses promoted across NTT Group companies. It aims to support the expansion of business activities in the space domain, further develop new markets, and contribute to the advancement of the space industry.

https://group.ntt/en/aerospace/
5NTT R&D FORUM 2025 IOWN ∴Quantum Leap Official website: https://www.rd.ntt/e/forum/2025/

6Kobayashi, D., Aoki, S., Sato,N. et al. Estimation of relative permittivity for measuring soil texture-dependent water content by GNSS-IR. GPS Solut 28, 210 (2024).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-024-01747-y
7NTT News release : Demonstration of a Ground Monitoring Method Using Optical Fibers for Early Detection of Road Collapse Risks
https://group.ntt/en/newsrelease/2025/10/21/251021a.html
About NTT
NTT contributes to a sustainable society through the power of innovation. We are a leading global technology company providing services to consumers and businesses as a mobile operator, infrastructure, networks, applications, and consulting provider. Our offerings include digital business consulting, managed application services, workplace and cloud solutions, data center and edge computing, all supported by our deep global industry expertise. We are over $90B in revenue and 340,000 employees, with $3B in annual R&D investments. Our operations span across 80+ countries and regions, allowing us to serve clients in over 190 of them. We serve over 75% of Fortune Global 100 companies, thousands of other enterprise and government clients and millions of consumers.
Media contact
NTT, Inc.
NTT Information Network Laboratory Group
Public Relations
Inquiry Form
Information is current as of the date of issue of the individual press release.
Please be advised that information may be outdated after that point.
NTT STORY
WEB media that thinks about the future with NTT