IOWN
Dissemination Activities
Dissemination Activities
IOWN Global Forum
The IOWN Global Forum is an international organization established to realize the IOWN
concept.
To realize the lofty goals of IOWN, it is necessary to unite the world's forces.
Collaboration is required at various levels, including technology, products, services, information, and
rules.
Companies and organizations participating in the IOWN Global Forum are not limited to ICT
providers. Many user companies and organizations participate in discussions on specific use cases for IOWN.
The unique feature of this project is that it examines the state of technology by delving into the thoughts
of each company.

Collaboration with international standardization organizations
For international information and communications services to be viable, component devices
must be interconnected internationally and operate as designed. Arrangements for interfaces between devices,
networks, and network operators are essential. International standardization bodies establish this agreement
across countries.
In particular, to spread IOWN technology throughout the world, whether in
developing or developed countries, it is important to cooperate with the de jure*1 standardization
organization, which influences regulations in each country, especially ITU-T*2, which is a de jure
standardization organization in the telecommunications field.
At the CxO Roundtable hosted by the
Director of ITU-T in December 2023, NTT proposed the importance of securing IOWN's international
connectivity and establishing de jure standards for global expansion, including in developing countries.
This proposal was approved by CxO and ITU-T executives from all over the world who attended the meeting, and
the IOWN Global Forum and ITU agreed to strengthen their relations. In the future, it will be important to
strengthen cooperation with international standardization organizations, especially ITU-T, to disseminate
IOWN.
*1 De jule
There are three broad categories of standards organizations (Figure
1).
De jure standards organizations: Standards created through official, written procedures that are
in force worldwide. According to the WTO agreement, only three organizations are in this category: ITU,
IEC, and ISO.
Regional and National Standards Bodies: Public standards bodies that establish
standards that apply only within specific regions or countries. Representative examples are the European
Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) and the Asia-Pacific Telecommunication Community (APT).
Standardization bodies in Japan include the Committee on Information and Communications Technology (TTC)
and the Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (ARIB).
Forum Organization: A standard created
by a forum formed by companies interested in a specific field. Although its effect is limited to the
members of the forum, the limited number of participants makes it possible to establish a standard with
appropriate granularity sooner. Typical examples include the Third Generation Partnership Project
(Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) and the IEEE.
*2 ITU-T
ITU (International Telecommunication Union) is one of the specialized
agencies of the United Nations and is a de jure*1 standardization organization. It is one of the few
international standardization organizations in which states are members, and currently has more than 190
member nations (companies and academic institutions can also join in addition to nations). ITU-T is the
telecommunications standardization arm of ITU and plays a very important role in international
standardization in the field of telecommunications. Typical international standards established by ITU-T
include E. 164, which specifies international telephone numbers, and H. 264, which specifies video
compression methods. Seizo Onoe, former Chief Technology Officer (CTO) of NTT DOCOMO and Chief
Standardization Strategy Officer (CSSO) of the holding company, is currently serving as ITU-T Director
(the first ITU-T Director from Japan).
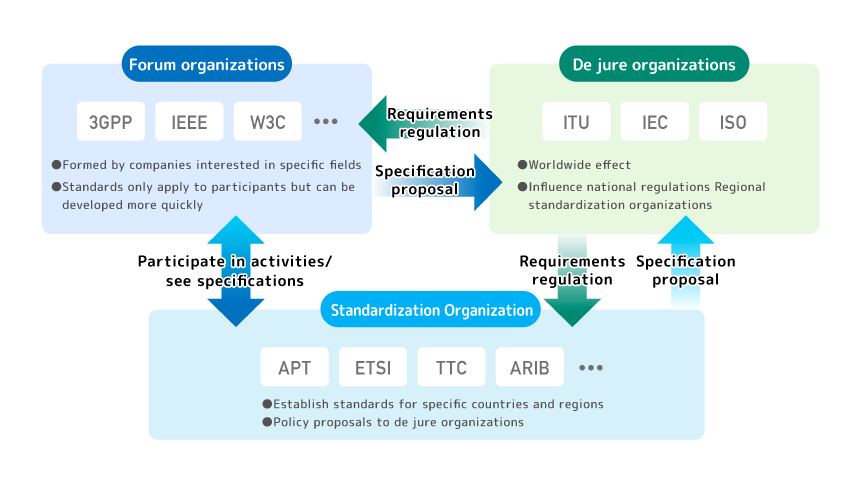
Figure 1 Standardization Organization