Microsoft ends support for Internet Explorer on June 16, 2022.
We recommend using one of the browsers listed below.
- Microsoft Edge(Latest version)
- Mozilla Firefox(Latest version)
- Google Chrome(Latest version)
- Apple Safari(Latest version)
Please contact your browser provider for download and installation instructions.
August 8, 2025
NTT, Inc.
Multi-Agent AI Technology Capable of Driving Complex Projects with Context-Aware Collaboration
- AI agents collaborating autonomously by reading intent through dialogue -
News Highlights:
- NTT has developed a foundational technology for autonomous and collaborative AI agents that, like humans, engage in dialogue to align their output expectations with others and work together to complete tasks.
- This technology is expected to enable AI agents to take on complex planning tasks that require consistency, feasibility, and specificity, such as developing integrated corporate branding strategies and formulating multifaceted business plans. These types of tasks have been difficult to solve with conventional technologies. The technology is also expected to contribute to continuous improvement of business operations.
- We will continue to advance research and development of autonomous AI-agent collaboration and work toward conducting a proof of concept (PoC) within the current fiscal year.
TOKYO - August 8, 2025 - NTT has developed a foundational technology for autonomous collaboration among AI agents. Like humans, the agents communicate through dialogue, align their expectations within the team, and work together to solve tasks collaboratively.
This technology enables high-quality solutions for complex planning tasks that require consistency, feasibility, and specificity while also meeting diverse needs. Such tasks have traditionally been difficult to address using conventional technologies. Example applications include the development of integrated corporate branding strategies that combine design, public relations, and marketing, as well as the creation of multifaceted business plans that address various customer perspectives simultaneously.
In addition, by reusing the knowledge accumulated through previous tasks, the system enables continuous improvement in task performance.
This achievement was presented on July 28, 2025, at ACL 2025, one of the most prestigious international conferences in the field of natural language processing.
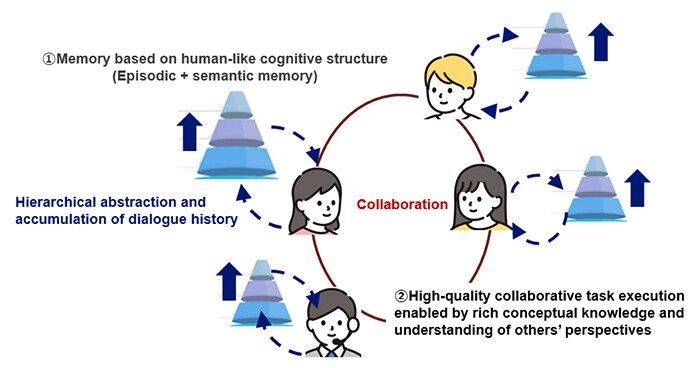 Figure 1 Key Features of the Foundational Technology for Autonomous Collaboration Among AI Agents
Figure 1 Key Features of the Foundational Technology for Autonomous Collaboration Among AI Agents
Background
In recent years, multi-agent systems, in which multiple AI agents collaborate to handle parts of business operations, have been attracting growing attention. In addition, multi-agent AI systems, where multiple specialized AI agents collaborate to handle interconnected subtasks within larger business processes, are attracting significant attention.
As a forward-looking initiative anticipating the evolution of such systems, research projects such as The Agent Company at Carnegie Mellon University are exploring the applicability of AI agents in real-world organizational operations. Furthermore, in OpenAI's roadmap for the evolution of generative AI, the concept of "AI-led organizational management" is presented as a final goal, and the vision of a future in which AI autonomously manages organizations is attracting increasing interest.
However, existing multi-agent AI systems typically assign divided subtasks to individual agents, making it difficult to maintain consistency across subtasks during task execution. While this approach works for routine tasks where subtasks are independent and can simply be combined, it struggles with complex tasks that require satisfying multiple, sometimes conflicting needs simultaneously. In such cases, AI agents face challenges in completing tasks with consistency, feasibility, and concreteness. This limitation hinders their ability to manage complex projects such as corporate strategy planning, which requires coordination across multiple departments, or multifaceted business planning involving diverse solutions.
In contrast, NTT has developed a foundational technology for autonomous collaboration among AI agents by enabling them to adopt human-inspired memory structures and co-creative processes. This allows the agents to solve complex tasks much like humans do, by continuously verifying and updating each other's problem-solving approaches and capabilities. Looking ahead, the technology aims to broadly address business planning tasks that will be essential when AI autonomously manages organizational operations in the future.
At NTT, in anticipation of a society where humans and AI work as partners in productive activities, we are conducting in research and development of AI Constellation. This approach enables AI agents to discuss and correct each other while offering diverse perspectives, collaboratively creating solutions with humans. The proposed technology was developed as one of the core components of an AI Constellation framework.
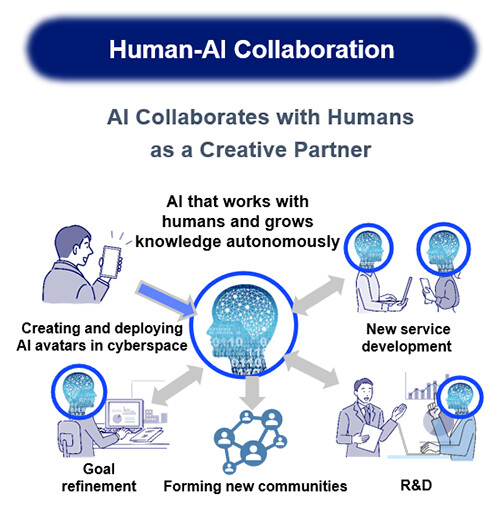 Figure 2 The "Human-AI Collaboration" Society Envisioned by NTT
Figure 2 The "Human-AI Collaboration" Society Envisioned by NTT
Research Results
In this technology, agents are first generated for each subtask derived from the complex task, and each agent builds knowledge related to its assigned subtask (Figure 3(a)). Human knowledge systems are supported by both individual experiences, known as episodic memory, and generalized facts, known as semantic memory. Our technology adopts a mechanism that enables AI agents to accumulate knowledge by combining these two types of memory.
Furthermore, this technology emulates the collaborative creation process found in human society, enabling agents to dynamically acquire and share knowledge with one another (Figure 3(b)(c)(d)). The system also generates expert agents with specialized knowledge necessary for task execution, which participate in discussions to acquire the required knowledge for problem-solving (Figure 3(c)). To address complex tasks, agents continuously update their understanding of their own and others' assigned subtasks and approaches through team and production meetings (Figure 3(b)(d)). They regularly align their task-solving strategies and collaboratively integrate diverse subtasks. This process leads to improvements in execution accuracy and the quality of solutions.
Our technology enables the generation of high-quality outputs even for complex planning tasks that require consistency, feasibility, and concreteness while satisfying diverse needs, such as formulating integrated corporate branding strategies combining design, public relations, and marketing, as well as developing multifaceted business plans that simultaneously address differing perspectives.
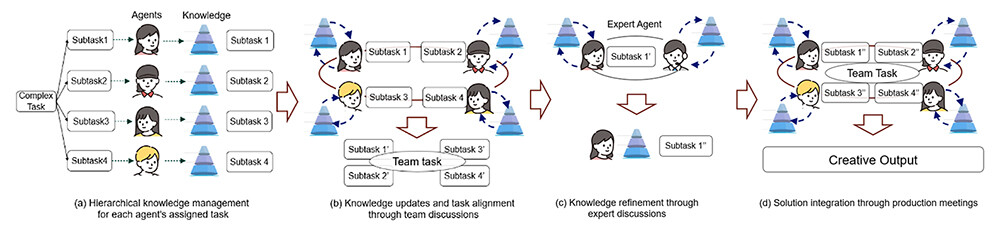 Figure 3 Overview of This Technology
Figure 3 Overview of This Technology
Technology Highlights
●Knowledge management inspired by human memory structure
AI agents acquire episodic memory through conversations with other agents, and progressively abstract this information into semantic memory to manage knowledge in a hierarchical manner. Repeated discussions based on this structured knowledge lead to the development of mutual understanding and enable productive discussion that incorporates diverse perspectives.
●Ensuring accuracy through cross-checking of knowledge
AI agents refine their knowledge by engaging in team meetings and conversations with expert agents possessing specialized knowledge. This process enables cross-checking of information between agents with different viewpoints, contributing to the overall accuracy of the final output.
●Improved task performance through agent reusability
By reusing agents that have accumulated knowledge and built mutual understanding through prior discussions, it becomes possible to continuously improve task performance in subsequent tasks.
Overview of the Experiment
In a series of experiments involving diverse creative document generation tasks, the proposed technology outperformed conventional methods in both automated and human evaluations.
For example, in a case study where agents were tasked with creating a business plan around the theme of tea, conventional methods simply listed solutions for each subtask without integrating or complementing them. In contrast, the proposed technology successfully consolidates the outputs by taking into account detailed information for each task and the content generated by other agents (Figure 4). This resulted in a well-rounded business plan (Figure 5) that addressed a wide range of customer needs. The final output included not only the development of various tea-related products but also experiential offerings, such as workshops on brewing techniques and flavor exploration, designed to enhance customer engagement.
Furthermore, when evaluating the AI generated proposal documents against multiple reference proposals prepared manually using ROUGE, the proposed method demonstrated an average score improvement of approximately 17.2 % compared to conventional methods.
These results demonstrate that the proposed technology can generate high-quality outputs through effective collaboration among AI agents.
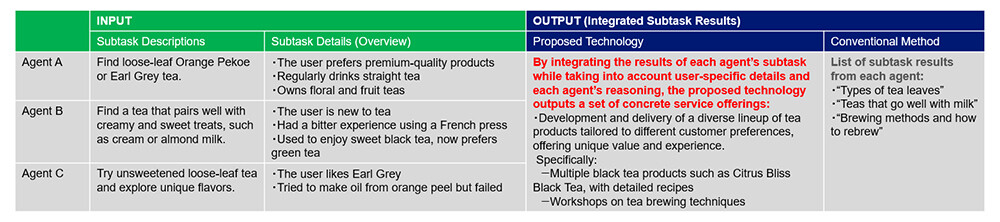 Figure 4 Comparison of Subtasks Addressed by Each Agent and the Integration Results of the Proposed and Conventional Methods
Figure 4 Comparison of Subtasks Addressed by Each Agent and the Integration Results of the Proposed and Conventional Methods
 Figure 5 Business Plan Generated by the Proposed Technology
Figure 5 Business Plan Generated by the Proposed Technology
Outlook
This achievement establishes a foundational technology for autonomous collaboration among AI agents, enabling them to solve complex tasks in a human-like manner. By incorporating human-inspired memory structures and co-creative processes, the agents can continuously assess and update each other's problem-solving approaches and capabilities. Moving forward, we will work toward conducting a PoC within the current fiscal year.
At the same time, we will accelerate our research and development to enable the practical use of AI agents in real business settings. Our focus will be on enabling AI to better capture human intent, such as incorporating user-directed improvements and adjustments into both final outputs and intermediate results. Through this, we aim to enhance creativity through effective collaboration between humans and AI.
About NTT
NTT contributes to a sustainable society through the power of innovation. We are a leading global technology company providing services to consumers and businesses as a mobile operator, infrastructure, networks, applications, and consulting provider. Our offerings include digital business consulting, managed application services, workplace and cloud solutions, data center and edge computing, all supported by our deep global industry expertise. We are over $90B in revenue and 340,000 employees, with $3B in annual R&D investments. Our operations span across 80+ countries and regions, allowing us to serve clients in over 190 of them. We serve over 75% of Fortune Global 100 companies, thousands of other enterprise and government clients and millions of consumers.
Media contact
NTT, Inc.
NTT Service Innovation Laboratory Group
Public Relations
Inquiry Form
Information is current as of the date of issue of the individual press release.
Please be advised that information may be outdated after that point.
NTT STORY
WEB media that thinks about the future with NTT










