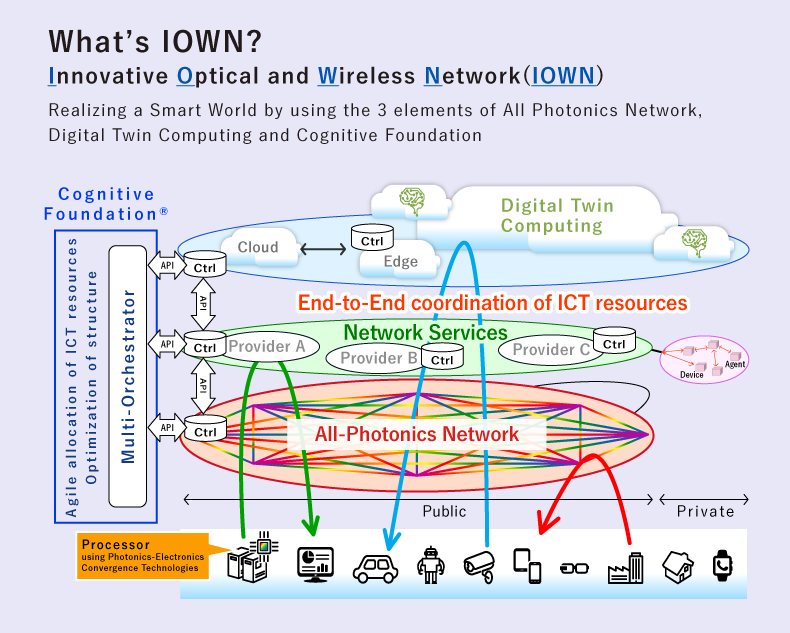
IOWN
Functions and Characteristics
Functions and Characteristics
Opticalization of networks and computers
IOWN takes on the challenge of creating a world of well being sustainably. The key is the introduction of optical technologies. It is highly energy-efficient compared to electricity and is an important factor in achieving both improved performance and sustainability. As the transmission capacity (frequency) of data increases, electricity consumes a large amount of energy even over short distances (Figure 1). In recent years, as capacity increased, it became important to convert electricity into light, for example, when transferring data between neighboring computers or even within computers.
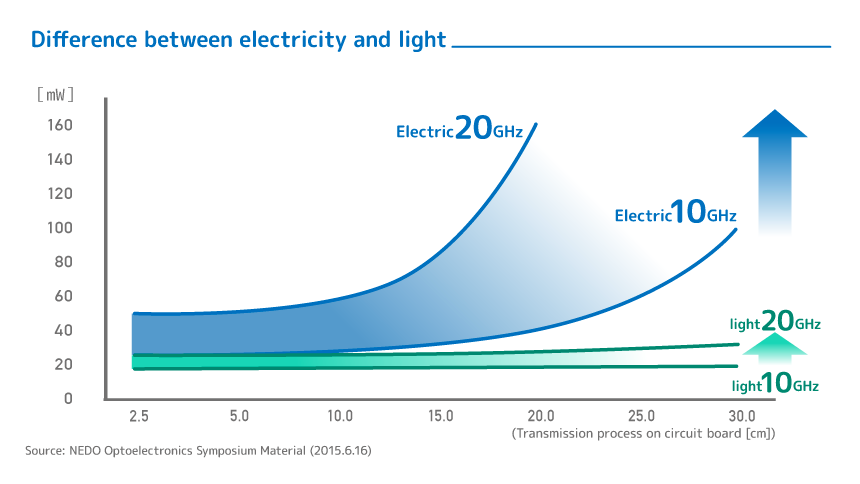
Figure 1 Low Power Consumption of Light
Simply replacing electricity with light will not achieve IOWN's lofty goals. It is
necessary to review network and computer systems. Many points that can be improved in terms of energy
efficiency in existing methods.
For example, in packet communication (TCP/IP protocol), which is
currently the mainstream network method, data is always divided into packets, and the destination is added
to each packet. Each point in the network (router) verifies the packet destination. This has to be switched
back to electricity, even if you‘re using fiber for transmission. The IOWN All-Photonics Network (APN)
rethinks this and completes all communications using optical communication without being switched back to
electricity. By eliminating the need for data division and electrical conversion, ultra-low latency networks
can be achieved.
Some improvements can also be made in computer architectures from the standpoint of energy efficiency. IOWN’s Data-Centric Infrastructure (DCI), which serves as the computing infrastructure for the IOWN era, can reduce power consumption through two approaches.
The first is disaggregated computing. A server is usually a single box filled with many components, but this approach breaks the system down so that the internal components can be shared. This allows you to combine and use only the components you need, such as CPUs and memory. It also enables you to turn off the power to components that are not in use, reducing power consumption. It is similar to first taking the system apart and then reorganizing it at the component level.
The second is photonics–electronics convergence. By replacing the electronic circuits that handle electrical signals with optical waveguides, DCI can reduce the power that was previously consumed by electrical wiring.
Overall optimization of different metrics
IOWN uses APN to transmit a far more variety and volume of information and process it
through ICT to understand the current state of the world and society in more detail and predict the future.
This will help to realize a world in which we can achieve well-being, but we are faced with the question of
whether a single evaluation function can express the good and bad of this world.
We believe that
conflicting values exist in this world and society in the form of competing values. We believe that it is
important to accept this contradiction and embrace diversity and that this is an important point in building
a world where we achieve well-being. We aim to achieve this by deriving solutions that are acceptable to
each of the different indicators, even if they are not optimal for each of them.
Digital Twin
Computing (DTC) is the key to achieving this. DTC is a technology that takes all the objects and phenomena
in the world as a Digital Twin, predicts the future through various simulations, and seeks a harmonious
solution, and psychology.
Observing, collecting, and using information on a large scale is no
easy task. To do this sustainably, flexible control of ICT resources is also crucial. In this role is the
Cognitive Foundation (CF), a set of functions that harmonize ICT resources holistically and optimally to
distribute the necessary information. It is a technology that enables information to be handled in
accordance with the location, application, environment, etc., without regard to the method or the operator.
Photonics-Electrics Convergence Devices and IOWN Roadmap
In the field of photonics-electrics convergence devices, we expect to see several leaps forward with this innovation. At IOWN1.0, we launched the All-Photonics Network (APN) service and achieved a delay target of 1/200 (Figure 2). The IOWN2.0 is a board-connected photoelectric device that advances the IOWN into the computer realm. It enables more flexible assembly of parts than ever before while achieving a highly energy-efficient computer. IOWN3.0 targets 125 times capacity and IOWN4.0 targets 100 times power efficiency. (Figures 2 and 3)
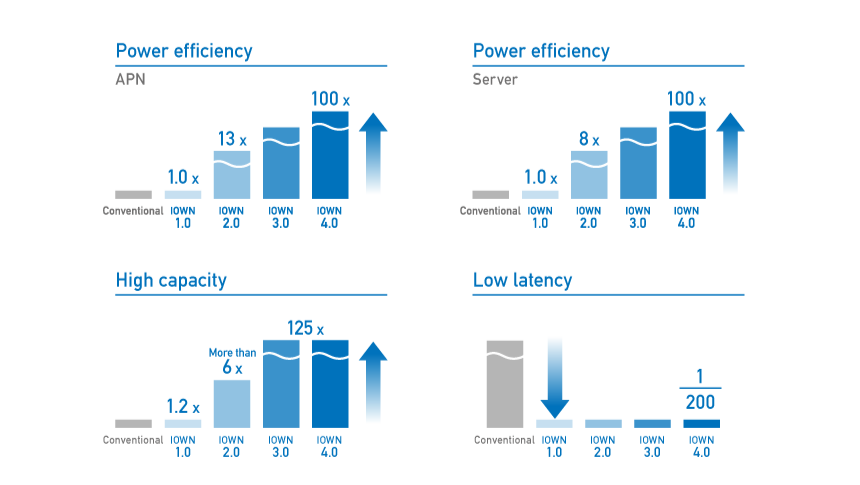
Figure 2 IOWN target performance
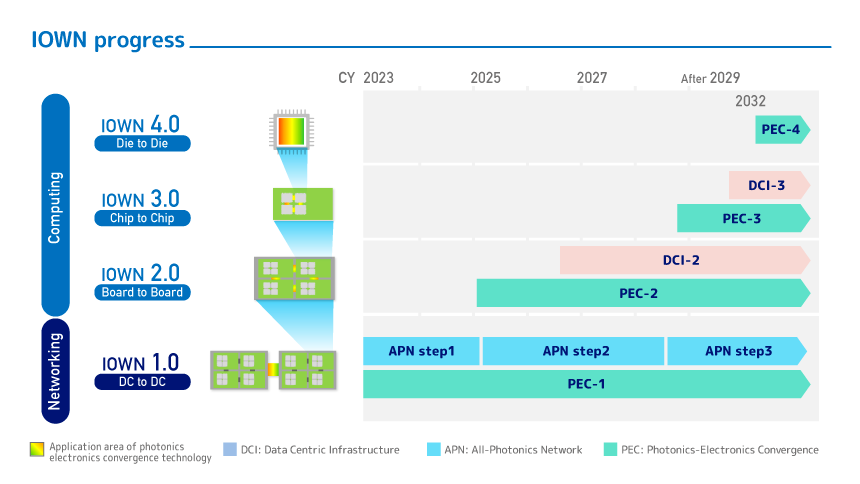
Figure 3 IOWN roadmap