Microsoft ends support for Internet Explorer on June 16, 2022.
We recommend using one of the browsers listed below.
- Microsoft Edge(Latest version)
- Mozilla Firefox(Latest version)
- Google Chrome(Latest version)
- Apple Safari(Latest version)
Please contact your browser provider for download and installation instructions.

Have you ever heard of digitization and digitalization?
While both terms are similar, the concepts are different. In this article, we will provide an overview of digitization and digitalization and how each relates to your business.
Table of Contents
- Difference between digitization and digitalization
- Businesses that will be affected by digitization
- Businesses affected by digitalization
- Agriculture evolving through digitization and digitalization
- NTT's approach to realizing smart agriculture
- NTT's departments and laboratories involved in this effort
Difference between digitization and digitalization
Digitization and digitalization are two words that are often confused because of their similarity. However, there are significant differences in what each entails.
Digitization means converting analog data into digital data. In this process, the existing business process is not modified and the digitization is performed while maintaining the existing state. An example could be having paper-based business processes digitized.
Digitization, on the other hand, uses digital technology to digitize business and manufacturing processes. Since the process may be fundamentally changed, it is not on the scale of a "department," but more like digitizing an entire company or workflow.
Each of these is explained in more detail below, with examples.
【Digitization】
Digitization refers to the process of converting physical information or data into a digital format.
By converting information in analog format (such as paper documents, photos or audio) into digital format (such as digital files, databases and e-books), information can be easily stored and shared.
Digitization improves accessibility and searchability of information, and enables efficient data management. For example, libraries scan and digitize old books, and companies convert paper contracts into electronic documents.
【Digitalization】
Digitalization is the process of using digital technology to improve business processes, services, and business models to increase efficiency and create new value.
Digitalization means more than just transforming data; it means transforming the efforts of organizations and individuals through the use of digital technology. Specifically, it refers to replacing traditional business processes with digital workflows to increase efficiency, and leveraging online platforms to provide new services.
Businesses that will be affected by digitization

There are many businesses that will be changed by digitization. Among them, the following areas are expected to see major changes:
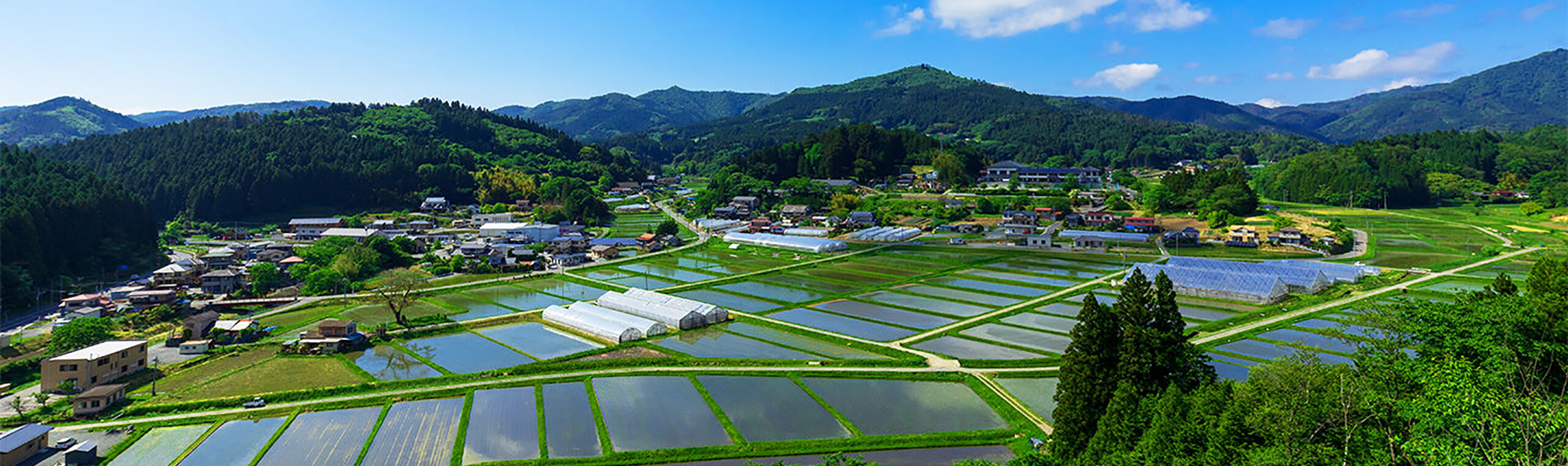
- Education
- Marketing
- Production and manufacturing
- Customer service
- Healthcare
- Entertainment
As business operations and content have moved online, and communication via chat and SNS has become mainstream, changes can be seen in a wide range of fields. However, these are just a few of the top areas. In reality, digitization is changing many different areas of business.
The progress of digitization requires flexible responses and strategic planning. In the healthcare industry, electronic medical records, telemedicine, and health monitoring have been advancing in recent years, and it is expected that we will see further changes in the future, such as increased safety and convenience.
Businesses affected by digitalization

On the other hand, digitalization will also affect most industries and businesses. It will affect the retail, financial, healthcare, and manufacturing industries, as well as the media and energy industries.
Digitalization is expected to improve productivity and service quality in many fields by developing online sales platforms, increasing the use of mobile payments, and automating manufacturing processes.
Agriculture evolving through digitization and digitalization

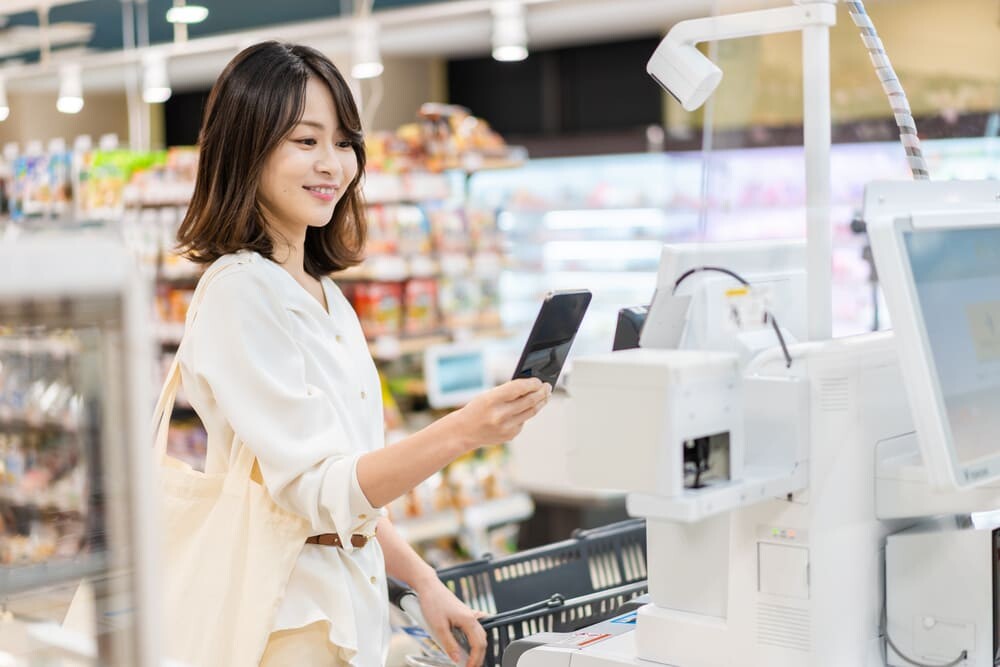
Agriculture is now evolving through both digitization and digitization. Digital mapping and GPS technology will enable precision agriculture, in which different fertilizers and watering are applied to each particular part of the field. This is expected to lead to more efficient use of resources and higher yields.
In addition, the process of creating agricultural products, from production to distribution, will be digitized to enhance quality control and traceability (the ability to track the movement of food). Consumers will be able to access information on the place of origin and production process, which will increase their confidence in food safety.
Other solutions include installing sensors and devices on farmland to collect real-time data, which can be analyzed and shared over a network to optimize agricultural processes. This is used in automated irrigation, livestock monitoring, and warehouse management.
Artificial intelligence (AI) based on digital data will be used to support decision-making, such as early prediction of pests and diseases and optimization of harvest time. This will improve productivity and sustainability in agriculture.
In recent years, the integration of IoT and agriculture has already given rise to a variety of examples. For example, looking at the use of "plastic greenhouses," which are common in agriculture where vegetables and fruits are grown, IoT has enabled visualization, thorough management, and situational awareness; all of them only possible with IoT.
Three points essential for the growth of crops--temperature, solar radiation, and humidity--are converted into data via cloud services. Each of these values, which are difficult to grasp manually, can be visualized and checked by the farmers themselves.
If abnormal values are detected, the farmer can quickly make decisions on how to respond, such as opening and closing the curtains inside the greenhouse or adjusting the temperature equipment, thereby avoiding total crop loss.
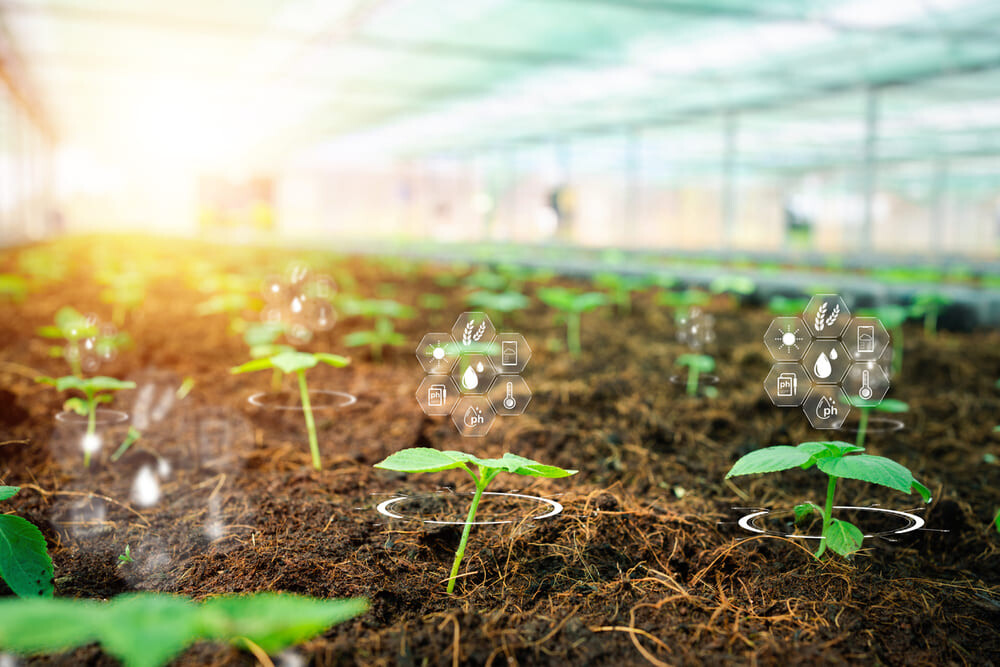

In addition, the status of the park can be monitored over the Internet through the cloud.
This eliminates the need for frequent patrols of the park, and will help reduce costs such as labor and personnel expenses.
Data recorded by IoT can be accumulated. Based on the accumulated data, it will be possible to control, plant, and stabilize quality, which will reduce damage and discoloration, common in agricultural products, and reduce damages.
Incidentally, the use of the accumulated data is not completed by the individual. For example, the data can be provided to agricultural associations for information sharing, or to successors or newcomers to the farming industry for data-based cultivation.
Japan is facing various challenges due to the declining population and labor shortage in the agricultural industry, but as mentioned above agriculture that utilizes IoT is beginning to move in the direction of solving these issues.
NTT's approach to realizing smart agriculture

NTT is working toward the realization of smart agriculture using cutting-edge technologies such as ICT and robots.
The recent issues in Japanese agriculture, such as labor shortages, the increase in abandoned farmland, and food loss, are expected to develop into social problems that will affect the stable supply of food. The know-how of domestic and overseas business partners with expertise in various fields related to agriculture, such as distributors and manufacturers, and NTT Group's ICT will be used to solve various issues in agriculture and create new value.
In addition, through collaboration with business partners, we are realizing a food and agriculture value chain that links all processes from production to consumption.
NTT Agri-Technology Corporation, NTT Group's only company specializing in primary industry--the sector of the economy that involves the extraction and collection of natural resources--is commercializing various initiatives in the fields of large-scale horticulture and land-based aquaculture under the slogan of "Creating New Forms of Primary Industry" while leveraging NTT Group assets and discovering new possibilities and values.
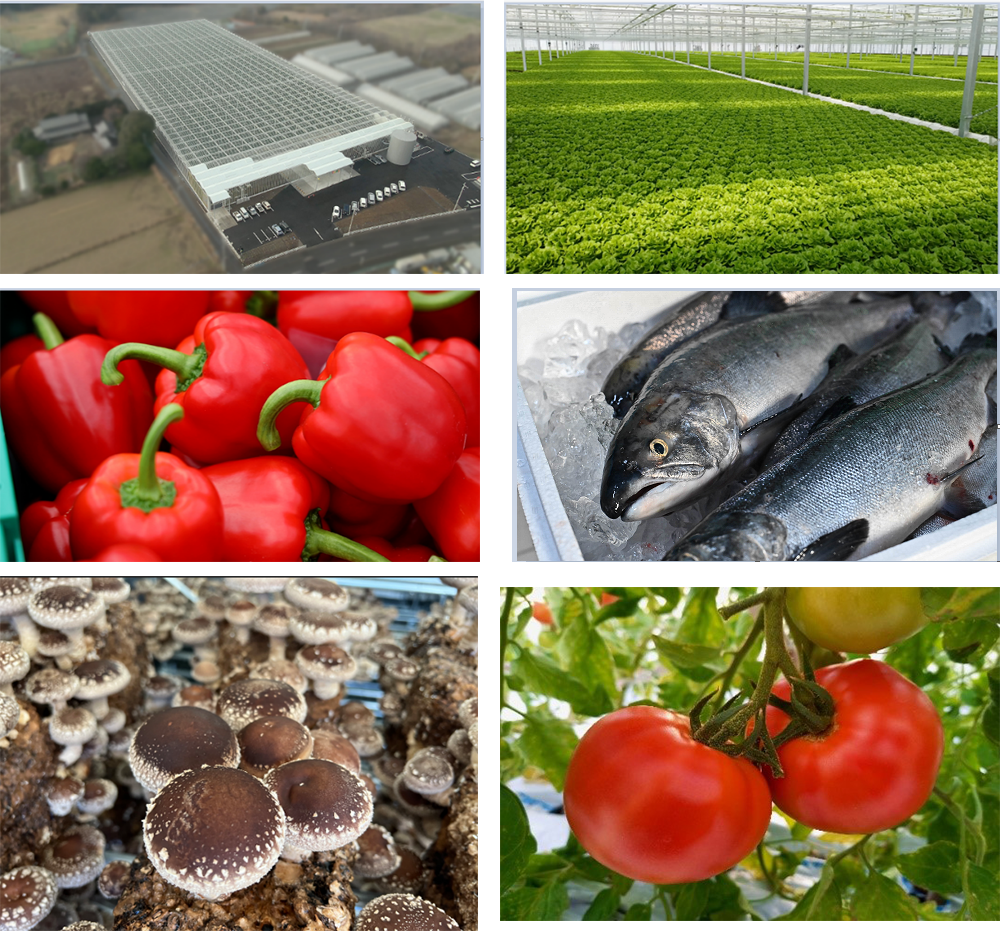

We are also involved in the design and construction of large-scale horticultural facilities using ICT-based environmental control (house engineering business), production and sales business in which we function as an agricultural corporation, and food value chain business in which we support the formation of production areas and regional development through the creation of sixth industrialization. The so-called "sixth industry" integrates the primary (agriculture, forestry, fisheries), secondary (processing and manufacturing), and tertiary (service and distribution) sectors to create added value and new business opportunities. We aim to make a contribution to regional development by creating an "agricultural eco-city" that integrates a variety of related industries with agriculture as the starting point.
Remote Farming Support enables farmers to receive accurate, data-driven guidance directly and frequently from a remote instructor, allowing them to engage in agriculture with peace of mind, without being limited by lack of experience or other factors.

To address the shortage of farmers, the company has also begun operating robots that can be controlled remotely to support field work.

As data is accumulated, yield prediction of agricultural products becomes possible. Advanced prediction results can be obtained by AI, based on a vast amount of accumulated data, including environmental and growth data, which will lead to efficient agriculture with less loss.
Furthermore, we also provide a service that allows easy management of people working in the field from a smartphone or tablet, leading to optimal personnel allocation and labor management, helping to increase productivity.

These efforts are based on NTT Group's strengths in communications technology, AI, IoT, and other know-how, and have been well received as a service that reflects the real needs of actual agricultural producers.
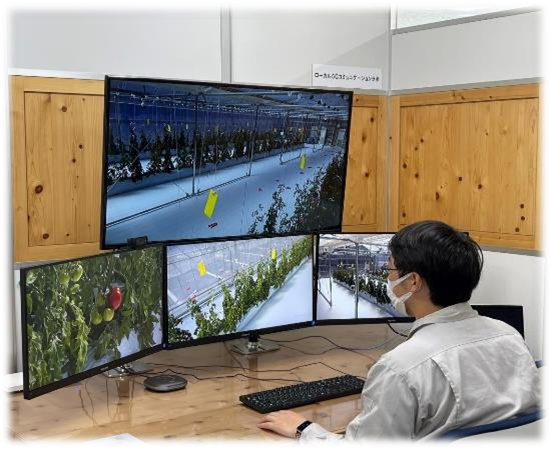

Agriculture is an important industry that has fostered local economies, cultures, and communities. In addition, risks to the stable supply of food are increasing, due to the changing global situation. Against this backdrop, NTT Agri-Technology will continue to play a role in responding to social needs.
NTT's departments and laboratories involved in this effort
NTT Agri-Technology Corporation
https://www.ntt-agritechnology.com/
NTT Group's approach to "Agriculture
https://group.ntt/jp/magazine/blog/agriculture/
In charge of Food and Agriculture Production, Research and Planning Division
Contact: ntt-agri@ntt.com